Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
Solution
| Electromagnet | Permanent magnet | ||
| 1. | It is a temporary magnet. |
1.
|
As the name suggests, it is a permanent magnet. |
| 2. | It can produce very strong magnetic force. | 2. | It produces a comparatively weak magnetic field. |
| 3. | Its polarity can be changed by changing the direction of current in the coil. | 3. | Its polarity is fixed and cannot be changed. |
| 4. | Its strength can be changed by changing the number of turns or by changing the current. | 4. | Its strength cannot be changed. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The magnetic flux through a loop varies according to the relation Φ = 8t2 + 6t + C, where ‘C’ is constant, 'Φ' is in milliweber and 't' is in second. What is the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in the loop at t = 2 seconds.
When Puja, a student of 10th class, watched her mother washing clothes in the open, she observed coloured soap bubbles and was curious to know why the soap bubbles appear coloured. In the evening when her father, an engineer by profession, came home, she asked him this question. Her father explained to her the basic phenomenon of physics due to which the soap bubbles appear coloured.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Puja and her father?
(b) State the phenomenon of light involved in the formation of coloured soap bubbles.
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
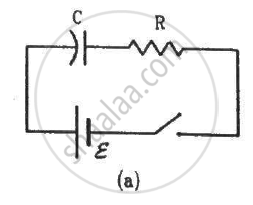
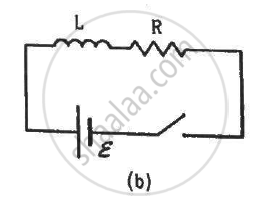
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
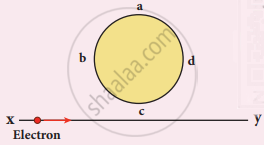
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
What for an inductor is used? Give some examples.
Give an illustration of determining direction of induced current by using Lenz’s law.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 4 A. If the magnetic flux through the coil is 6 x 10-5 Wb, find the magnetic energy stored in the medium surrounding the coil.
We can induce the current in a coil by ____________.
An expression for oscillating electric field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given as Ez = 300 sin(5π × 103x - 3π × 1011t)Vm-1 Then, the value of magnetic field amplitude will be ______. (Given: speed of light in Vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
