Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
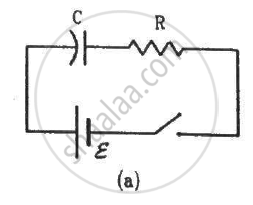
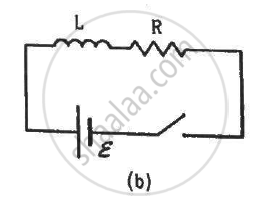
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
Solution
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
The charge on the capacitor at time ''t'' after connecting it with a battery is given by,
`Q=C epsilon[1-e^(-t"/RC")]`
Just after t = 0, the charge on the capacitor will be
`Q=C epsilon[1-e^0]=0`
For a long after time, t → ∞
Thus, the charge on the capacitor will be
`Q = Cepsilon[1-e^(-infty)]`
`rArr Q=Cepsilon[1-0]=Cepsilon`
The current in the inductor at time ''t'' after closing the switch is given by
`I=V_b/R(1-e^(-tR"/L"))`
Just before the time t0, current through the inductor is given by
`I=V_b/R(1-e^(-t_0R"/L"))`
It is given that the time t0 is very long.
∴ t0 → ∞
`I=epsilon/R(1-e^-infty)=epsilon/R`
When the switch is opened, the current through the inductor after a long time will become zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
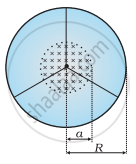
A line charge λ per unit length is lodged uniformly onto the rim of a wheel of mass M and radius R. The wheel has light non-conducting spokes and is free to rotate without friction about its axis (Figure). A uniform magnetic field extends over a circular region within the rim. It is given by,
B = − B0 k (r ≤ a; a < R)
= 0 (otherwise)
What is the angular velocity of the wheel after the field is suddenly switched off?
Name two devices in which electromagnets are used and two devices where permanent magnets are used.
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A motor works on the principle electric generator?
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
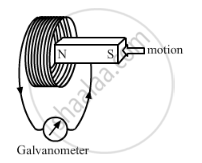
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A loop of wire is held near a magnet.
Welders wear special glass goggles while working. Why? Explain.
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
List two ways of increasing the strength of an electromagnet if the material of the electromagnet is fixed.
Write Fleming’s right hand thumb rule with the help of diagram.
A straight metal wire crosses a magnetic field of flux 4 mWb in a time 0.4 s. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the wire.
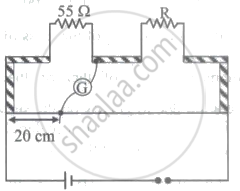
Shown in the figure below is a metre bridge set up with null deflection in the galvanometer. The value of the unknown resistance R is ______
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
Which of the following instruments works by electromagnetic induction?
A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
The primary of a transformer has 400 turns while the secondary has 2000 turns. If the power output from the secondary at 1000 Vis 12 kW, what is the primary voltage?
