Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
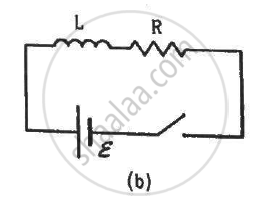
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
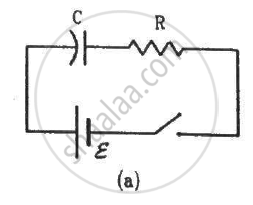
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
उत्तर
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
The charge on the capacitor at time ''t'' after connecting it with a battery is given by,
`Q=C epsilon[1-e^(-t"/RC")]`
Just after t = 0, the charge on the capacitor will be
`Q=C epsilon[1-e^0]=0`
For a long after time, t → ∞
Thus, the charge on the capacitor will be
`Q = Cepsilon[1-e^(-infty)]`
`rArr Q=Cepsilon[1-0]=Cepsilon`
The current in the inductor at time ''t'' after closing the switch is given by
`I=V_b/R(1-e^(-tR"/L"))`
Just before the time t0, current through the inductor is given by
`I=V_b/R(1-e^(-t_0R"/L"))`
It is given that the time t0 is very long.
∴ t0 → ∞
`I=epsilon/R(1-e^-infty)=epsilon/R`
When the switch is opened, the current through the inductor after a long time will become zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loud speaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area 2 cm2 with 25 closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the field region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick 90° turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in the coil (measured by a ballistic galvanometer connected to coil) is 7.5 mC. The combined resistance of the coil and the galvanometer is 0.50 Ω. Estimate the field strength of magnet.
If ‘R’ is the radius of dees and ‘B’ be the magnetic field of induction in which positive charges (q) of mass (m) escape from the cyclotron, then its maximum speed (vmax) is _______.
A) `(qR)/(Bm)`
B)`(qm)/(Br)`
C) `(qBR)/m`
D) `m/(qBR)`
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A motor works on the principle electric generator?
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
The current is stopped in a wire held near a loop of wire .
Welders wear special glass goggles while working. Why? Explain.
Fig. shows a simple form of an A.C. generator.

(a) Name the parts labeled A and B.
(b) What would be the effect of doubling the number of turns on the coil if the speed of rotation remains unchanged?
(c) Which of the output terminals is positive if the coil is rotating in the
direction shown in the diagram (anticlockwise)?
( d ) What is the position of the rotating coil when p.d. across its ends is zero? Explain why p.d. is zero when the coil is at this position .
(e) Sketch a graph showing how the p.d. across the ends of the rotating coil varies with time for an A.C. dynamo.
( f) On th e same sheet of paper and vertically below the first graph using the same time scale, sketch graphs to show the effect of
(i) Doubling the speed of rotation and at the same time keeping
the field and the number of turns constant,
(ii ) Doubling the number of turns on the coil and at the same time
doubling the speed of rotation of the coil, keeping th e speed
constant.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
Transformer______.
Why soft iron is preferred to be used as the core of the electromagnet of an electric bell?
The right-hand thumb rule is also called _______ rule.
Write Fleming’s right hand thumb rule with the help of diagram.
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
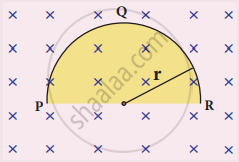
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
A straight metal wire crosses a magnetic field of flux 4 mWb in a time 0.4 s. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the wire.
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
A cylindrical bar magnet (A) and similar unmagnetized cylindrical iron bar (B) are dropped through metallic pipe. The time taken to come down by ____________.
A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
