Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
उत्तर
(a) The quantity \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] can also be written as :-
\[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}=V......\text(V = Voltage)\]
Unit of voltage is J/C.
Voltage can be written as:-
`"Voltage"="Energy"/"Charge"`
Dimensions of energy = [ML2T-2]
Dimensions of charge = [IT]
Thus, the dimensions of voltage can be written as:
[ML2T-2] ×[IT]−1 = [ML2I−1T−3]
(b) The quantity vBl is the product of quantities v, B and L.
Dimensions of velocity v = [LT−1]
Dimensions of length l = [L]
The dimensions of magnetic field B can be found using the following formula:-
`B=F/(qv)`
Dimensions of force F = [MLT−2]
Dimensions of charge q = [IT]
Dimensions of velocity = [LT−1]
The dimensions of a magnetic field can be written as:
MI−1T−2
∴ Dimensions of vBl = [LT−1] × [MI−1T−2] × [L]= [ML2I−1T−3]
(c) The quantity \[\frac{d\phi}{dt}\] is equal to the emf induced; thus, its dimensions are the same as that of the voltage.
Voltage can be written as:-
`"Voltage"="Energy"/"Charge"`
Dimensions of energy = [ML2T-2]
Dimensions of charge = [IT]
The dimensions of voltage can be written as:
[ML2T-2] ×[IT]−1 = [ML2I−1T−3]
∴ Dimensions of \[\frac{d\phi}{dt}=ML^2I^{−1}T^{−3}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Electric field intensity in free space at a distance ‘r’ outside the charged conducting sphere of radius ‘R’ in terms of surface charge density ‘ a ’ is............................
(a)`sigma / in_0[R/r]^2`
(b)`in_0/sigma[R/r]^2`
(c)`R/r[sigma/in_0]^2`
(d)`R/sigma[r/in_0]^2`
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
When current is 'switched on' and 'switched off' in a coil, a current is induced in another coil kept near it. What is this phenomenon known as?
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
The current is stopped in a wire held near a loop of wire .
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
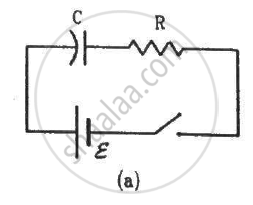
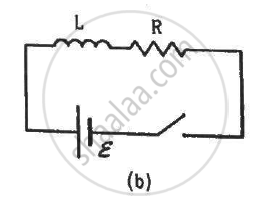
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
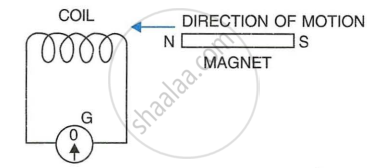
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
What is an electromagnet? List any two uses.
Choose the correct option:
A conductor rod of length (l) is moving with velocity (v) in a direction normal to a uniform magnetic field (B). What will be the magnitude of induced emf produced between the ends of the moving conductor?
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4 A is ______
The right-hand thumb rule is also called _______ rule.
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
Name some equipment that uses electromagnetism for functioning.
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
A conducting bar of length L is free to slide on two parallel conducting rails as shown in the figure
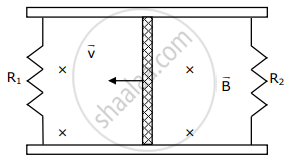
Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected across the ends of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` pointing into the page. An external agent pulls the bar to the left at a constant speed v. The correct statement about the directions of induced currents I1 and I2 flowing through R1 and R2 respectively is:
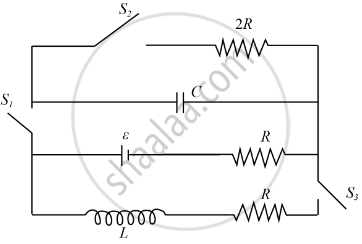
In the given circuit, initially switch S1 is closed and S2 and S3 are open. After charging of capacitor, at t = 0, S1 is open and S2 and S3 are closed. If the relation between inductance capacitance and resistance is L = 4CR2 then the time (in sec) after which current passing through capacitor and inductor will be same is ______ × 10-4 N. (Given R = ℓn(2)mΩ, L = 2mH)
Show that for a given positive ion species in a cyclotron, (i) the radius of their circular path inside a dee is directly proportional to their speed, and (ii) the maximum ion energy achievable is directly proportional to the square of the magnetic induction.
