Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
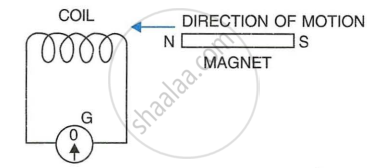
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
उत्तर
-
- When the magnet is moved rapidly in the direction of arrow, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes and there is a deflection in the galvanometer, indicating a flow of current through the coil.
- On keeping the magnet still, the magnetic flux linked with the coil does not change and there is no deflection in the galvanometer, indicating that no current is flowing through the coil.
- When the magnet is rapidly pulled out, there is again change in the magnetic flux linked with the coil and the galvanometer shows a deflection but this time in opposite direction, indicating that a current is flowing in opposite direction in the coil.
- If a more powerful magnet is used, deflection in the galvanometer will be large, indicating a greater amount of current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name a common device that uses electromagnets.
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
Explain why, the core of an electromagnet should be of soft iron and not of steel.
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
The diagram 10 shows two coils X and Y. The coil X is connected to a battery S and a key K. The coil Y is connected to a galvanometer G.
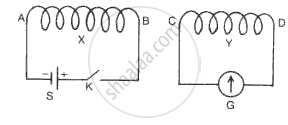
When the key K is closed. State the polarity
(i)At the end of the coil X,
(ii)At the end C of the coil Y,
(iii)At the end C of the coil Y if the coil Y is (a) Moved towards the coil X, (b) Moved away from the coil X.
Draw a labelled diagram to make an electromagnet from a soft iron bar. Mark the polarity at its ends in your diagram. What precaution would you observe while making it?
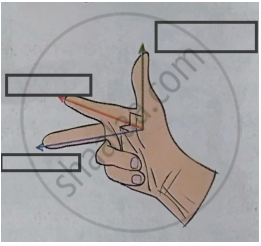
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
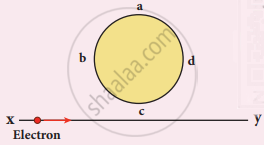
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
A metal plate can be heated by ______.
A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
