Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
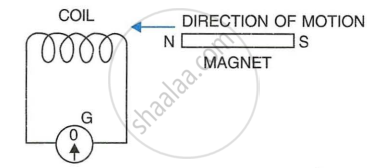
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
उत्तर
-
- When the magnet is moved rapidly in the direction of arrow, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes and there is a deflection in the galvanometer, indicating a flow of current through the coil.
- On keeping the magnet still, the magnetic flux linked with the coil does not change and there is no deflection in the galvanometer, indicating that no current is flowing through the coil.
- When the magnet is rapidly pulled out, there is again change in the magnetic flux linked with the coil and the galvanometer shows a deflection but this time in opposite direction, indicating that a current is flowing in opposite direction in the coil.
- If a more powerful magnet is used, deflection in the galvanometer will be large, indicating a greater amount of current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
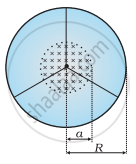
A line charge λ per unit length is lodged uniformly onto the rim of a wheel of mass M and radius R. The wheel has light non-conducting spokes and is free to rotate without friction about its axis (Figure). A uniform magnetic field extends over a circular region within the rim. It is given by,
B = − B0 k (r ≤ a; a < R)
= 0 (otherwise)
What is the angular velocity of the wheel after the field is suddenly switched off?
The magnetic flux through a loop is varying according to a relation `phi = 6t^2 + 7t + 1` where `phi` is in milliweber and t is in second. What is the e.m.f. induced in the loop at t = 2 second?
Write some of the important uses of electromagnets.
When Puja, a student of 10th class, watched her mother washing clothes in the open, she observed coloured soap bubbles and was curious to know why the soap bubbles appear coloured. In the evening when her father, an engineer by profession, came home, she asked him this question. Her father explained to her the basic phenomenon of physics due to which the soap bubbles appear coloured.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Puja and her father?
(b) State the phenomenon of light involved in the formation of coloured soap bubbles.
A conducting square loop having edges of length 2.0 cm is rotated through 180° about a diagonal in 0.20 s. A magnetic field B exists in the region which is perpendicular to the loop in its initial position. If the average induced emf during the rotation is 20 mV, find the magnitude of the magnetic field.
List two ways of increasing the strength of an electromagnet if the material of the electromagnet is fixed.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
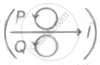
Metal rings P and Q are lying in the same plane, where current I is increasing steadily. The induced current in metal rings is shown correctly in figure.
A metal plate can be heated by ______.
Which of the following instruments works by electromagnetic induction?
