Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The magnetic flux through a loop is varying according to a relation `phi = 6t^2 + 7t + 1` where `phi` is in milliweber and t is in second. What is the e.m.f. induced in the loop at t = 2 second?
उत्तर
Given : `phi = 6t^2 + 7t + 1` (in milliweber),t=2s
find: Magnitude of induced e.m.f. (e)
formula: `e=(dphi)/dt` (in magnitude)
Calculation: Using formula
`e=d/dt(6t^2+7t+1)`
`=12t+7`
At t=2s
`|e|=12 xx 2 + 7`
`=31mV=31xx10^-3V`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
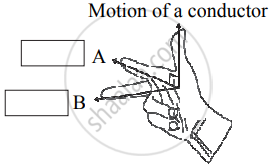
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loud speaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area 2 cm2 with 25 closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the field region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick 90° turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in the coil (measured by a ballistic galvanometer connected to coil) is 7.5 mC. The combined resistance of the coil and the galvanometer is 0.50 Ω. Estimate the field strength of magnet.
A line charge λ per unit length is lodged uniformly onto the rim of a wheel of mass M and radius R. The wheel has light non-conducting spokes and is free to rotate without friction about its axis (Figure). A uniform magnetic field extends over a circular region within the rim. It is given by,
B = − B0 k (r ≤ a; a < R)
= 0 (otherwise)
What is the angular velocity of the wheel after the field is suddenly switched off?
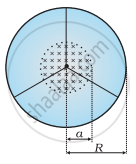
If ‘R’ is the radius of dees and ‘B’ be the magnetic field of induction in which positive charges (q) of mass (m) escape from the cyclotron, then its maximum speed (vmax) is _______.
A) `(qR)/(Bm)`
B)`(qm)/(Br)`
C) `(qBR)/m`
D) `m/(qBR)`
When an electric current is passed through any wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. Then why an electric iron connecting cable does not attract nearby iron objects when electric current switched on through it?
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be:
(a) north pole
(b) east pole
(c) south pole
(d) west pole
What condition is necessary for the production of current by electromagnetic induction?
What do you understand by the term "electromagnetic induction"? Explain with the help of a diagram.
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
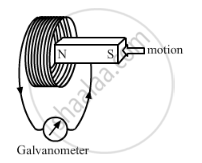
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
The current is stopped in a wire held near a loop of wire .
The coil of a moving-coil galvanometer keeps on oscillating for a long time if it is deflected and released. If the ends of the coil are connected together, the oscillation stops at once. Explain.
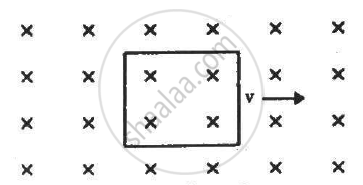
A conducting square loop of side l and resistance R moves in its plane with a uniform velocity v perpendicular to one of its sides. A uniform and constant magnetic field Bexists along the perpendicular to the plane of the loop as shown in figure. The current induced in the loop is _____________ .
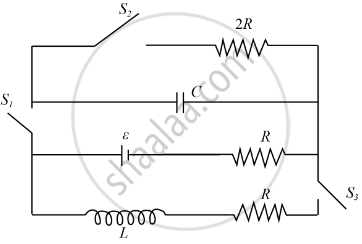
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
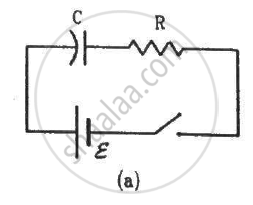
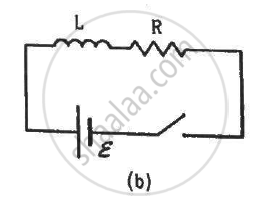
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
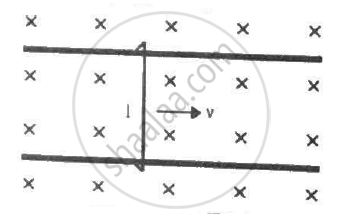
Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation l. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
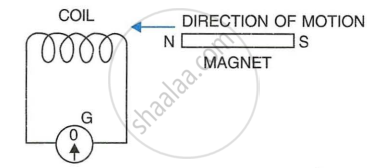
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
Transformer______.
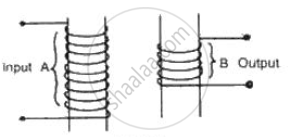
Complete the following diagram of a transformer and name the parts labeled A and B. Name the part you have drawn to complete the diagram . What is the material of this part? In this transformer a step-up or step-down? Why?
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
What is an electromagnet? List any two uses.
List two ways of increasing the strength of an electromagnet if the material of the electromagnet is fixed.
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
State the condition at which we say the two coils kept close to each other are perfectly coupled with each other.
Using Ampere's law, obtain an expression for the magnetic induction near a current-carrying straight infinitely long wire.
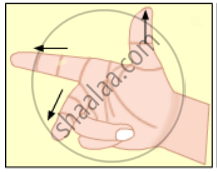
Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
Which of the following scientist invented the rule of electromagnetic induction?
Fleming's left hand rule : electric current : : Fleming's right hand rule : _______
Write Fleming’s right hand thumb rule with the help of diagram.
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Right hand thumb rule.
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
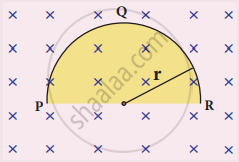
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
What for an inductor is used? Give some examples.
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
Give an illustration of determining direction of induced current by using Lenz’s law.
Show that Lenz’s law is in accordance with the law of conservation of energy.
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
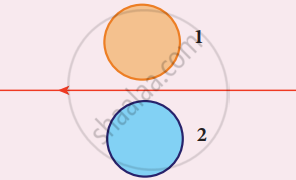
Metal rings P and Q are lying in the same plane, where current I is increasing steadily. The induced current in metal rings is shown correctly in figure.
A layer of atmosphere that reflects medium frequency radio waves which is ineffective during night, is ______.
A metal plate can be heated by ______.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
What will be observed when the Magnet starts oscillating through the coil. Explain the reason behind this observation.
Which of the following instruments works by electromagnetic induction?
Sea turtles return to their birth beach many decades after they were born due to ______.
A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2×10 -3T. Find the force on the conductor.
In the given circuit, initially switch S1 is closed and S2 and S3 are open. After charging of capacitor, at t = 0, S1 is open and S2 and S3 are closed. If the relation between inductance capacitance and resistance is L = 4CR2 then the time (in sec) after which current passing through capacitor and inductor will be same is ______ × 10-4 N. (Given R = ℓn(2)mΩ, L = 2mH)
An expression for oscillating electric field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given as Ez = 300 sin(5π × 103x - 3π × 1011t)Vm-1 Then, the value of magnetic field amplitude will be ______. (Given: speed of light in Vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
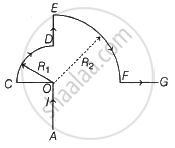
In the current carrying conductor (AOCDEFG) as shown, the magnetic induction at point O is ______.
(R1 and R2 are radii of CD and EF respectively. l = current in the loop, μ0 = permeability of free space)
When an electric current is passed through a wire or a coil, a magnetic field is produced. Is the reverse phenomenon possible i.e, can a magnetic field produce an electric current? Explain with the help of an appropriate example.
