Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using Ampere's law, obtain an expression for the magnetic induction near a current-carrying straight infinitely long wire.
उत्तर
- Consider a long straight wire carrying a current I as shown in the figure below.
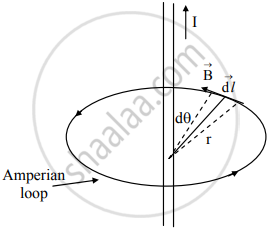
A long straight current-carrying wire
`vec"B"` and `vec"d""l"` are tangential to the Amperian loop which in this case is a circle.
∴ `vec"B"` . `vec"d""l" = "B dl"`
= B r dθ - The field `vec"B"` at a distance r from the wire is given by
B = `mu_0/(2pi) "I"/"r"`
∴ `oint_"c" vec"B".vec"d""l" = int_0^(2pi) (mu_0 "I")/(2pi "r") "r d" theta = mu_0 "I"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The magnetic flux through a loop varies according to the relation Φ = 8t2 + 6t + C, where ‘C’ is constant, 'Φ' is in milliweber and 't' is in second. What is the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in the loop at t = 2 seconds.
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
Prove theoretically (electromagnetic induction) `e = (dphi)/(dt)`
An emf of 2V is induced in a coil when the current in it is changed from 0A to 10A in 0·40 sec. Find the coefficient of self-inductance of the coil.
What is an electromagnet? Describe the construction and working of an electromagnet with the help of a labelled diagram.
Explain why, an electromagnet is called a temporary magnet.
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be:
(a) north pole
(b) east pole
(c) south pole
(d) west pole
The most suitable material for making the core of an electromagnet is:
(a) soft iron
(b) brass
(c) aluminium
(d) steel
What condition is necessary for the production of current by electromagnetic induction?
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A motor works on the principle electric generator?
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
A light metal disc on the top of an electromagnet is thrown up as the current is switched on. Why? Give reason.
The coil of a moving-coil galvanometer keeps on oscillating for a long time if it is deflected and released. If the ends of the coil are connected together, the oscillation stops at once. Explain.
L, C and R represent the physical quantities inductance, capacitance and resistance respectively. Which of the following combinations have dimensions of frequency?
(a) `1/(RC)`
(b) `R/L`
(c) `1/sqrt(LC)`
(d) C/L
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
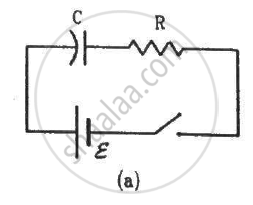
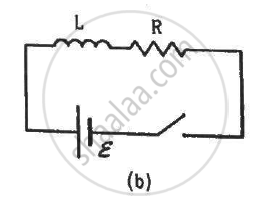
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
A conducting square loop having edges of length 2.0 cm is rotated through 180° about a diagonal in 0.20 s. A magnetic field B exists in the region which is perpendicular to the loop in its initial position. If the average induced emf during the rotation is 20 mV, find the magnitude of the magnetic field.
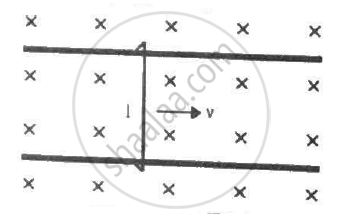
Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation l. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
Can a transformer work when it is connected to a D.C. source? Give a reason.
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-down transformer.
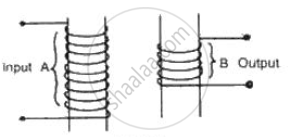
Complete the following diagram of a transformer and name the parts labeled A and B. Name the part you have drawn to complete the diagram . What is the material of this part? In this transformer a step-up or step-down? Why?
What is an electromagnet? List any two uses.
Draw a labelled diagram to show how an electromagnet is made.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
List two ways of increasing the strength of an electromagnet if the material of the electromagnet is fixed.
List some of the practical applications of an electromagnet.
Why soft iron is preferred to be used as the core of the electromagnet of an electric bell?
You have been provided with a solenoid AB.
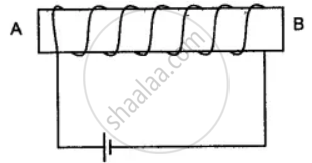
(i) What is the polarity at end A?
(ii) Give one advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
Choose the correct option:
A conductor rod of length (l) is moving with velocity (v) in a direction normal to a uniform magnetic field (B). What will be the magnitude of induced emf produced between the ends of the moving conductor?
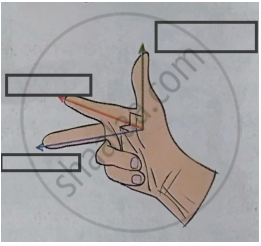
Fleming's left hand rule : electric current : : Fleming's right hand rule : _______
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
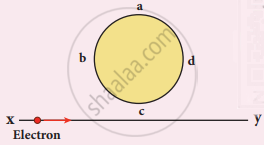
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
State Lenz’s law.
What for an inductor is used? Give some examples.
Show that Lenz’s law is in accordance with the law of conservation of energy.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
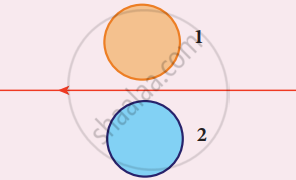
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
A layer of atmosphere that reflects medium frequency radio waves which is ineffective during night, is ______.
A cylindrical bar magnet is kept along the axis of a circular coil. If the magnet is rotated about its axis, then ____________.
A cylindrical bar magnet (A) and similar unmagnetized cylindrical iron bar (B) are dropped through metallic pipe. The time taken to come down by ____________.
The instrument that use to defect electric current in the circuit is known as ____________.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
What will be observed when the Magnet starts oscillating through the coil. Explain the reason behind this observation.
Name some equipment that uses electromagnetism for functioning.
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
The primary of a transformer has 400 turns while the secondary has 2000 turns. If the power output from the secondary at 1000 Vis 12 kW, what is the primary voltage?
The charge will flow through a galvanometer of resistance 200Ω connected to a 400Ω circular coil of 1000 turns wound on a wooden stick 20 mm in diameter, if a magnetic field B = 0.012 T parallel to the axis of the stick decreased suddenly to zero, is near ______.
