Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Choose the correct option:
A conductor rod of length (l) is moving with velocity (v) in a direction normal to a uniform magnetic field (B). What will be the magnitude of induced emf produced between the ends of the moving conductor?
पर्याय
BLv
BLv2
`1/2Blv`
`(2Bl)/v`
उत्तर
BLv
Explanation:
Step 1:
Let F = Force on charge q due to the motion of rod in the field
Therefore, `F = qVB` .....(1)
Where, q = charge on body (i.e. rod)
v = velocity of rod
B = Magnetic Field on the rod
Step 2:
This force on the charge is attributed to the induced electric field E
Therefore, `Eq = F` ......(2)
Substitute the values from (1) and (2) and calculate:
`E = V B` .....(3)
Therefore, an electric field `E = V B` is said to be induced in the rod due to the motion in the magnetic field.
Potential difference due to the field = emf induced (e) = Electric Field x Length
= `El`
Using (3),
e = `V Bl`
संबंधित प्रश्न
Electric field intensity in free space at a distance ‘r’ outside the charged conducting sphere of radius ‘R’ in terms of surface charge density ‘ a ’ is............................
(a)`sigma / in_0[R/r]^2`
(b)`in_0/sigma[R/r]^2`
(c)`R/r[sigma/in_0]^2`
(d)`R/sigma[r/in_0]^2`
A solenoid of length 1.5 m and 4 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns per metre. A current of 5 A is flowing through it. The magnetic induction at a point inside the solenoid along the axis is ............................. .
(μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am)
- π × 10-5 T
- 2π × 10-5 T
- 3π × 10-5 T
- 4π × 10-5 T
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
A metal rod `1/sqrtpi `m long rotates about one of its ends perpendicular to a plane whose magnetic induction is 4 x 10-3 T. Calculate the number of revolutions made by the rod per second if the e.m.f. induced between the ends of the rod is 16 mV.
When a bar magnet is pushed towards (or away) from the coil connected to a galvanometer, the pointer in the galvanometer deflects. Identify the phenomenon causing this deflection and write the factors on which the amount and direction of the deflection depends. State the laws describing this phenomenon.
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
The magnetic flux through a loop is varying according to a relation `phi = 6t^2 + 7t + 1` where `phi` is in milliweber and t is in second. What is the e.m.f. induced in the loop at t = 2 second?
Name two devices in which electromagnets are used and two devices where permanent magnets are used.
Explain why, the core of an electromagnet should be of soft iron and not of steel.
Write some of the important uses of electromagnets.
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be:
(a) north pole
(b) east pole
(c) south pole
(d) west pole
What condition is necessary for the production of current by electromagnetic induction?
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
Describe different ways to induce current in a coil of wire.
Describe one experiment to demonstrate the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
The current is stopped in a wire held near a loop of wire .
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A loop of wire is held near a magnet.
A light metal disc on the top of an electromagnet is thrown up as the current is switched on. Why? Give reason.
L, C and R represent the physical quantities inductance, capacitance and resistance respectively. Which of the following combinations have dimensions of frequency?
(a) `1/(RC)`
(b) `R/L`
(c) `1/sqrt(LC)`
(d) C/L
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-down transformer.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
A. C. generator______.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
Transformer______.
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
Answer the following:
State the principles of the electric motor and electric generator.
What is an electromagnet? List any two uses.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
List two ways of increasing the strength of an electromagnet if the material of the electromagnet is fixed.
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
Draw a labelled diagram to make an electromagnet from a soft iron bar. Mark the polarity at its ends in your diagram. What precaution would you observe while making it?
The diagram shows a rectangular coil ABCD, suspended freely between the concave pole pieces of a permanent horseshoe magnet, such that the plane of the coil is parallel to the magnetic field.

(i) State your observation, when current is switched on.
(ii) Give an explanation for your observation in (i).
(iii) State the rule, which will help you to find the motion of rotation of coil.
(iv) In which position will the coil ultimately come to rest?
(v) State four ways of increasing the magnitude of force acting on the coil.
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4 A is ______
Which of the following scientist invented the rule of electromagnetic induction?
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
What for an inductor is used? Give some examples.
Give an illustration of determining direction of induced current by using Lenz’s law.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 0.4 A. If the magnetic flux of 4 mWb is linked with each turn of the coil, find the inductance of the coil.
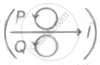
Metal rings P and Q are lying in the same plane, where current I is increasing steadily. The induced current in metal rings is shown correctly in figure.
A cylindrical bar magnet (A) and similar unmagnetized cylindrical iron bar (B) are dropped through metallic pipe. The time taken to come down by ____________.
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
A rectangular, a square, a circular and an elliptical loop, all in the (x - y) plane, are moving out of a uniform magnetic field with a constant velocity `vecv = vhati`. The magnetic field is directed along the negative z-axis direction. The induced emf, during the passage of these loops, out of the field region, will not remain constant for ______.
A conducting bar of length L is free to slide on two parallel conducting rails as shown in the figure
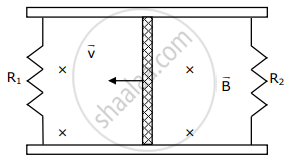
Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected across the ends of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` pointing into the page. An external agent pulls the bar to the left at a constant speed v. The correct statement about the directions of induced currents I1 and I2 flowing through R1 and R2 respectively is:
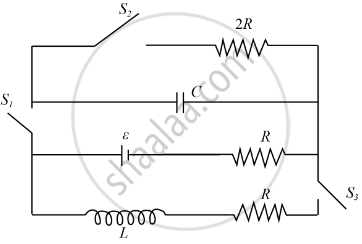
In the given circuit, initially switch S1 is closed and S2 and S3 are open. After charging of capacitor, at t = 0, S1 is open and S2 and S3 are closed. If the relation between inductance capacitance and resistance is L = 4CR2 then the time (in sec) after which current passing through capacitor and inductor will be same is ______ × 10-4 N. (Given R = ℓn(2)mΩ, L = 2mH)
A current I = 10 sin(100π t) A is passed in first coil, which induces a maximum e.m.f of 5π volt in second coil. The mutual inductance between the coils is ______.
The charge will flow through a galvanometer of resistance 200Ω connected to a 400Ω circular coil of 1000 turns wound on a wooden stick 20 mm in diameter, if a magnetic field B = 0.012 T parallel to the axis of the stick decreased suddenly to zero, is near ______.
Show that for a given positive ion species in a cyclotron, (i) the radius of their circular path inside a dee is directly proportional to their speed, and (ii) the maximum ion energy achievable is directly proportional to the square of the magnetic induction.
