Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A solenoid of length 1.5 m and 4 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns per metre. A current of 5 A is flowing through it. The magnetic induction at a point inside the solenoid along the axis is ............................. .
(μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am)
- π × 10-5 T
- 2π × 10-5 T
- 3π × 10-5 T
- 4π × 10-5 T
उत्तर
2π × 10-5 T
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Electric field intensity in free space at a distance ‘r’ outside the charged conducting sphere of radius ‘R’ in terms of surface charge density ‘ a ’ is............................
(a)`sigma / in_0[R/r]^2`
(b)`in_0/sigma[R/r]^2`
(c)`R/r[sigma/in_0]^2`
(d)`R/sigma[r/in_0]^2`
The magnetic flux through a loop varies according to the relation Φ = 8t2 + 6t + C, where ‘C’ is constant, 'Φ' is in milliweber and 't' is in second. What is the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in the loop at t = 2 seconds.
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
A metal rod `1/sqrtpi `m long rotates about one of its ends perpendicular to a plane whose magnetic induction is 4 x 10-3 T. Calculate the number of revolutions made by the rod per second if the e.m.f. induced between the ends of the rod is 16 mV.
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
If ‘R’ is the radius of dees and ‘B’ be the magnetic field of induction in which positive charges (q) of mass (m) escape from the cyclotron, then its maximum speed (vmax) is _______.
A) `(qR)/(Bm)`
B)`(qm)/(Br)`
C) `(qBR)/m`
D) `m/(qBR)`
A circular coil of cross-sectional area 200 cm2 and 20 turns is rotated about the vertical diameter with angular speed of 50 rad s−1 in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 3.0 × 10−2T. Calculate the maximum value of the current in the coil.
An emf of 2V is induced in a coil when the current in it is changed from 0A to 10A in 0·40 sec. Find the coefficient of self-inductance of the coil.
When an electric current is passed through any wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. Then why an electric iron connecting cable does not attract nearby iron objects when electric current switched on through it?
State three ways in which the strength of an electromagnet can be increased.
Name two devices in which electromagnets are used and two devices where permanent magnets are used.
Write some of the important uses of electromagnets.
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be:
(a) north pole
(b) east pole
(c) south pole
(d) west pole
When current is 'switched on' and 'switched off' in a coil, a current is induced in another coil kept near it. What is this phenomenon known as?
What do you understand by the term "electromagnetic induction"? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Describe different ways to induce current in a coil of wire.
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A loop of wire is held near a magnet.
A light metal disc on the top of an electromagnet is thrown up as the current is switched on. Why? Give reason.
A conducting rod is moved with a constant velocity v in a magnetic field. A potential difference appears across the two ends _____________ .
L, C and R represent the physical quantities inductance, capacitance and resistance respectively. Which of the following combinations have dimensions of frequency?
(a) `1/(RC)`
(b) `R/L`
(c) `1/sqrt(LC)`
(d) C/L
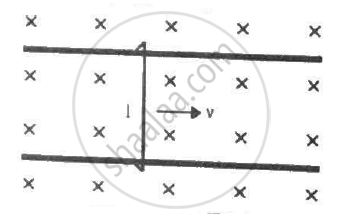
Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation l. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
Can a transformer work when it is connected to a D.C. source? Give a reason.
Draw and label the diagram of a simple D.C. motor.
(a) Explain the rotation of the coil, giving a reason for your answer.
(b) How can you reverse the direction of rotation of the armature?
(c) How can you increase the speed of rotation of the motor?
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
D.C. motor ______.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
Transformer______.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
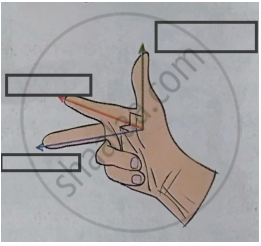
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
What is an electromagnet? List any two uses.
Draw a labelled diagram to show how an electromagnet is made.
Draw a labelled diagram to make an electromagnet from a soft iron bar. Mark the polarity at its ends in your diagram. What precaution would you observe while making it?
You have been provided with a solenoid AB.
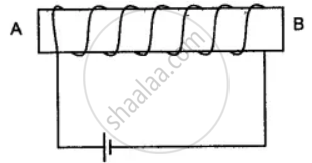
(i) What is the polarity at end A?
(ii) Give one advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
The right-hand thumb rule is also called _______ rule.
Write Fleming’s right hand thumb rule with the help of diagram.
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
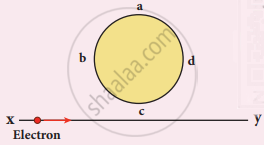
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
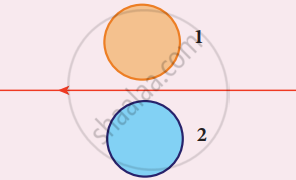
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
The instrument that use to defect electric current in the circuit is known as ____________.
What should be the core of an electromagnet?
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
The working of a dynamo is based on the principle of
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
One solenoid is centered inside another. The outer one has a length of 50.0 cm and contains 6750 coils, while the coaxial inner solenoid is 3.0 cm long and π cm2 in area and contains 150 coils. The current in the outer solenoid is changing at 3000 A/s. The emf induced in the inner solenoid is ______ V.
(Round off to two decimal places.)
An expression for oscillating electric field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given as Ez = 300 sin(5π × 103x - 3π × 1011t)Vm-1 Then, the value of magnetic field amplitude will be ______. (Given: speed of light in Vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
The primary of a transformer has 400 turns while the secondary has 2000 turns. If the power output from the secondary at 1000 Vis 12 kW, what is the primary voltage?
The charge will flow through a galvanometer of resistance 200Ω connected to a 400Ω circular coil of 1000 turns wound on a wooden stick 20 mm in diameter, if a magnetic field B = 0.012 T parallel to the axis of the stick decreased suddenly to zero, is near ______.
