Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A solenoid of length 1.5 m and 4 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns per metre. A current of 5 A is flowing through it. The magnetic induction at a point inside the solenoid along the axis is ............................. .
(μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am)
- π × 10-5 T
- 2π × 10-5 T
- 3π × 10-5 T
- 4π × 10-5 T
Solution
2π × 10-5 T
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
A metal rod `1/sqrtpi `m long rotates about one of its ends perpendicular to a plane whose magnetic induction is 4 x 10-3 T. Calculate the number of revolutions made by the rod per second if the e.m.f. induced between the ends of the rod is 16 mV.
Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loud speaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area 2 cm2 with 25 closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the field region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick 90° turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in the coil (measured by a ballistic galvanometer connected to coil) is 7.5 mC. The combined resistance of the coil and the galvanometer is 0.50 Ω. Estimate the field strength of magnet.
The magnetic flux through a loop is varying according to a relation `phi = 6t^2 + 7t + 1` where `phi` is in milliweber and t is in second. What is the e.m.f. induced in the loop at t = 2 second?
Prove theoretically (electromagnetic induction) `e = (dphi)/(dt)`
When an electric current is passed through any wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. Then why an electric iron connecting cable does not attract nearby iron objects when electric current switched on through it?
Explain why, the core of an electromagnet should be of soft iron and not of steel.
State the factors on which the strength of an electromagnet depends. How does it depend on these factors?
The north-south polarities of an electromagnet can be found easily by using:
(a) Fleming's right-hand rule
(b) Fleming's left-hand rule
(c) Clock face rule
(d) Left-hand thumb rule
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be:
(a) north pole
(b) east pole
(c) south pole
(d) west pole
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
Name one device which works on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
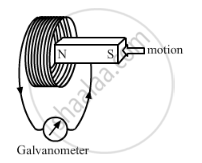
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
Describe one experiment to demonstrate the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
Welders wear special goggles or face masks with glass windows to protect their eyes from electromagnetic radiations. Name the radiations and write the range of their frequency.
Show diagrammatically how an alternating emf is generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rotating loop.
L, C and R represent the physical quantities inductance, capacitance and resistance respectively. Which of the following combinations have dimensions of frequency?
(a) `1/(RC)`
(b) `R/L`
(c) `1/sqrt(LC)`
(d) C/L
A conducting square loop having edges of length 2.0 cm is rotated through 180° about a diagonal in 0.20 s. A magnetic field B exists in the region which is perpendicular to the loop in its initial position. If the average induced emf during the rotation is 20 mV, find the magnitude of the magnetic field.
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-down transformer.
Draw and label the diagram of a simple D.C. motor.
(a) Explain the rotation of the coil, giving a reason for your answer.
(b) How can you reverse the direction of rotation of the armature?
(c) How can you increase the speed of rotation of the motor?
Fig. shows a simple form of an A.C. generator.

(a) Name the parts labeled A and B.
(b) What would be the effect of doubling the number of turns on the coil if the speed of rotation remains unchanged?
(c) Which of the output terminals is positive if the coil is rotating in the
direction shown in the diagram (anticlockwise)?
( d ) What is the position of the rotating coil when p.d. across its ends is zero? Explain why p.d. is zero when the coil is at this position .
(e) Sketch a graph showing how the p.d. across the ends of the rotating coil varies with time for an A.C. dynamo.
( f) On th e same sheet of paper and vertically below the first graph using the same time scale, sketch graphs to show the effect of
(i) Doubling the speed of rotation and at the same time keeping
the field and the number of turns constant,
(ii ) Doubling the number of turns on the coil and at the same time
doubling the speed of rotation of the coil, keeping th e speed
constant.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
D.C. motor ______.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
A. C. generator______.
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
List two ways of increasing the strength of an electromagnet if the material of the electromagnet is fixed.
Why soft iron is preferred to be used as the core of the electromagnet of an electric bell?
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
Draw a labelled diagram to make an electromagnet from a soft iron bar. Mark the polarity at its ends in your diagram. What precaution would you observe while making it?
Which of the following scientist invented the rule of electromagnetic induction?
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Show that Lenz’s law is in accordance with the law of conservation of energy.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
The magnetic flux passing through a coil perpendicular to its plane is a function of time and is given by OB = (2t3 + 4t2 + 8t + 8) Wb. If the resistance of the coil is 5 Ω, determine the induced current through the coil at a time t = 3 second.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 4 A. If the magnetic flux through the coil is 6 x 10-5 Wb, find the magnetic energy stored in the medium surrounding the coil.
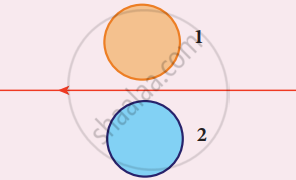
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
A cylindrical bar magnet is kept along the axis of a circular coil. If the magnet is rotated about its axis, then ____________.
We can induce the current in a coil by ____________.
What should be the core of an electromagnet?
For making a strong electromagnet the material of the core should be ______.
A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
Which of the following phenomena makes use of electromagnetic induction?
A conducting bar of length L is free to slide on two parallel conducting rails as shown in the figure
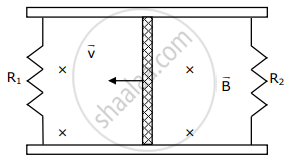
Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected across the ends of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` pointing into the page. An external agent pulls the bar to the left at a constant speed v. The correct statement about the directions of induced currents I1 and I2 flowing through R1 and R2 respectively is:
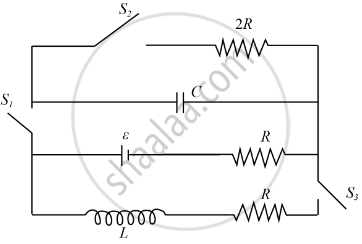
In the given circuit, initially switch S1 is closed and S2 and S3 are open. After charging of capacitor, at t = 0, S1 is open and S2 and S3 are closed. If the relation between inductance capacitance and resistance is L = 4CR2 then the time (in sec) after which current passing through capacitor and inductor will be same is ______ × 10-4 N. (Given R = ℓn(2)mΩ, L = 2mH)
The charge will flow through a galvanometer of resistance 200Ω connected to a 400Ω circular coil of 1000 turns wound on a wooden stick 20 mm in diameter, if a magnetic field B = 0.012 T parallel to the axis of the stick decreased suddenly to zero, is near ______.
