Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
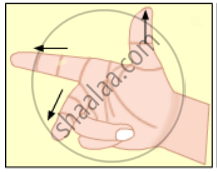
Solution
Fleming's right-hand rule
It represents Fleming's right-hand rule used for finding the direction of induced current with respect to the directions of the magnetic field and motion of the conductor.

The direction of current induced in a conductor can be obtained by holding the thumb, the index finger, and the middle finger of your right hand mutually perpendicular to each other. In this situation, the thumb indicates the direction of the motion of the conductor, the index finger points along the magnetic field, and the middle finger points along the current induced in the conductor.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An emf of 2V is induced in a coil when the current in it is changed from 0A to 10A in 0·40 sec. Find the coefficient of self-inductance of the coil.
When an electric current is passed through any wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. Then why an electric iron connecting cable does not attract nearby iron objects when electric current switched on through it?
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
Explain why, an electromagnet is called a temporary magnet.
Explain why, the core of an electromagnet should be of soft iron and not of steel.
State the factors on which the strength of an electromagnet depends. How does it depend on these factors?
Write some of the important uses of electromagnets.
The north-south polarities of an electromagnet can be found easily by using:
(a) Fleming's right-hand rule
(b) Fleming's left-hand rule
(c) Clock face rule
(d) Left-hand thumb rule
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be:
(a) north pole
(b) east pole
(c) south pole
(d) west pole
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
Name one device which works on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
Welders wear special goggles or face masks with glass windows to protect their eyes from electromagnetic radiations. Name the radiations and write the range of their frequency.
A light metal disc on the top of an electromagnet is thrown up as the current is switched on. Why? Give reason.
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
Fig. shows a simple form of an A.C. generator.

(a) Name the parts labeled A and B.
(b) What would be the effect of doubling the number of turns on the coil if the speed of rotation remains unchanged?
(c) Which of the output terminals is positive if the coil is rotating in the
direction shown in the diagram (anticlockwise)?
( d ) What is the position of the rotating coil when p.d. across its ends is zero? Explain why p.d. is zero when the coil is at this position .
(e) Sketch a graph showing how the p.d. across the ends of the rotating coil varies with time for an A.C. dynamo.
( f) On th e same sheet of paper and vertically below the first graph using the same time scale, sketch graphs to show the effect of
(i) Doubling the speed of rotation and at the same time keeping
the field and the number of turns constant,
(ii ) Doubling the number of turns on the coil and at the same time
doubling the speed of rotation of the coil, keeping th e speed
constant.
Complete the following diagram of a transformer and name the parts labeled A and B. Name the part you have drawn to complete the diagram . What is the material of this part? In this transformer a step-up or step-down? Why?
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
Using Ampere's law, obtain an expression for the magnetic induction near a current-carrying straight infinitely long wire.
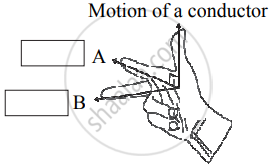
Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
What for an inductor is used? Give some examples.
A closely wound circular coil of radius 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field. When the magnetic field is changed from 8000 T to 2000 T in 6 s, an emf of 44 V is induced in it. Calculate the number of turns in the coil.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 4 A. If the magnetic flux through the coil is 6 x 10-5 Wb, find the magnetic energy stored in the medium surrounding the coil.
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
A layer of atmosphere that reflects medium frequency radio waves which is ineffective during night, is ______.
A cylindrical bar magnet (A) and similar unmagnetized cylindrical iron bar (B) are dropped through metallic pipe. The time taken to come down by ____________.
A generator has an e.m.f. of 440 Volt and internal resistance of 4000 hm. Its terminals are connected to a load of 4000 ohm. The voltage across the load is ______.
What should be the core of an electromagnet?
Induced current flows through a coil ______.
For making a strong electromagnet the material of the core should be ______.
A coil of one turn is made of a wire of certain length and then from the same length, a coil of two turns is made. If the same current is passed in both the cases, then the ratio of the magnetic inductions at their centres will be:
A conducting bar of length L is free to slide on two parallel conducting rails as shown in the figure
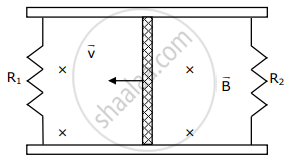
Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected across the ends of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` pointing into the page. An external agent pulls the bar to the left at a constant speed v. The correct statement about the directions of induced currents I1 and I2 flowing through R1 and R2 respectively is:
The primary of a transformer has 400 turns while the secondary has 2000 turns. If the power output from the secondary at 1000 Vis 12 kW, what is the primary voltage?
