Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is a solenoid? Compare the magnetic field produced by a solenoid with the magnetic field of a bar magnet. Draw neat figures and name various components.
Solution
A solenoid is a long straight insulated wire, such as a copper coil, often wrapped around a cylinder-shaped body. The diameter of the solenoid is lesser than its length. It produces a magnetic field when electric current is passed through it.
Magnetic field produced by a solenoid is shown below:

Magnetic field produced by a bar magnet is shown below:
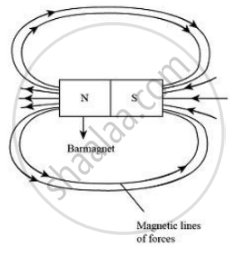
On comparing field lines produced by a solenoid with that produced by a bar magnet, we observe that they are very much identical. Thus, a solenoid acts as a bar magnet when current is passed through it.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The back face of a circular loop of wire is found to be south magnetic pole. The direction of current in this face of the circular loop of wire will be:
(a) towards south
(b) clockwise
(c) anticlockwise
(d) towards north
Draw a labelled diagram showing the three magnetic field lines of a loop carrying current. Mark the direction of current and the direction of magnetic field by arrows in your diagram.
A wire, bent into a circle, carries current in an anticlockwise direction. What polarity does this face of the coil exhibit?
What is the direction of magnetic field at the centre of a coil carrying current in clockwise ?
What is the direction of magnetic field at the centre of a coil carrying current in the anticlockwise direction?
Which of the statement given below correctly describes the magnetic field near a long, straight current carrying conductor?
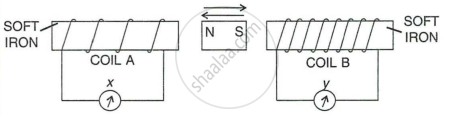
A magnet kept at the centre of two coils A and B is moved to and fro as shown in the diagram. The two galvanometers show deflection. State with a reason whether : x > y or x< y [x and y are magnitudes of deflection.]
Answer the following question.
Explain with the help of the pattern of magnetic field lines the distribution of the magnetic field due to a current-carrying a circular loop.
Answer the following question:
Why is it that the magnetic field of a current-carrying coil having n turns, is 'n' times as large as that produced by a single turn (loop)?
State and illustrate the rule used for finding the polarity of the faces of a circular coil.
An induced emf is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil. The magnitude of induced emf does not depend on ____________.
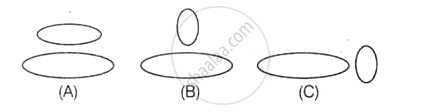
If two circular coils can be arranged in any of the three situations as shown in the diagrams below, then their mutual induction will be:
The nature of magnetic field line passing through the centre of current carrying circular loop is ____________.
Why does a magnetic compass needle pointing North and South in the absence of a nearby magnet get deflected when a bar magnet or a current carrying loop is brought near it. Describe some salient features of magnetic lines of field concept.
Explain with the help of a labelled diagram the distribution of magnetic field due to a current through a circular loop. Why is it that if a current carrying coil has n turns the field produced at any point is n times as large as that produced by a single turn?
Explain the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. Describe an experiment to show that a current is set up in a closed loop when an external magnetic field passing through the loop increases or decreases.
The correct pattern of magnetic field lines of the field produced by a current carrying circular loop is:
