HSC Science (General)
HSC Science (Electronics)
HSC Science (Computer Science)
Academic Year: 2013-2014
Date: October 2013
Advertisements
Draw a diagram showing all components of forces acting on a vehicle moving on a curved banked road.
Chapter: [0.01] Circular Motion
Write the necessary equation for maximum safety, speed and state the significance of each term involved in it.
Chapter: [0.01] Circular Motion
Explain Maxwell distribution of molecular speed with necessary graph.
Chapter: [0.09] Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
Find the total energy and binding energy of an artificial satellite of mass 800 kg orbiting at a height of 1800 km above the surface of the earth.
[G = 6.67 x 10-11 S.I. units, Radius of earth : R = 6400 km, Mass of earth : M = 6 x 1024 kg]
Chapter: [0.02] Gravitation
Wavelengths of two notes in the air are`[70/153]^m` and `[70/157]^m`. Each of these notes produces 8 beats per second with a tuning fork of fixed frequency. Find the velocity of sound in the air and frequency of the tuning fork.
Chapter: [0.06] Superposition of Waves [0.07] Wave Motion [0.1] Wave Theory of Light
Draw a diagram showing different stages of projection for artificial satellite.
Chapter: [0.02] Gravitation
State the law of conservation of angular momentum and explain with a suitable example.
Chapter: [0.01] Rotational Dynamics
Define the angle of contact.
Chapter: [0.02] Mechanical Properties of Fluids [0.06] Surface Tension
State any two characteristics of the angle of contact
Chapter: [0.02] Mechanical Properties of Fluids [0.06] Surface Tension
Draw a neat labelled diagram for Ferry's perfectly black body.
Chapter: [0.09] Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
A stone of mass 5 kg. tied to one end of a rope of length 0.8 m, is whirled in a vertical circle. Find the minimum velocity at the highest point and at the midway point.
[g = 9.8 m/s2]
Chapter: [0.01] Circular Motion
The maximum velocity of a particle performing linear S.H.M. is 0.16 m/s. If its maximum acceleration is 0.64 m/s2, calculate its period.
Chapter: [0.04] Oscillations [0.05] Oscillations
Water rises to a height 3.2 cm in a glass capillary tube. Find the height to which the same water will rise in another glass capillary having half area of cross section.
Chapter: [0.02] Mechanical Properties of Fluids [0.06] Surface Tension
A 36 cm long sonometer wire vibrates with frequency of 280 Hz in fundamental mode, when it is under tension of 24.5 N. Calculate linear density of the material of wire.
Chapter: [0.12] Electrostatics
A thin wire of length L and uniform linear mass density r is bent into a circular coil. M. I. of the coil about tangential axis in its plane is ................................
- `(3rhoL^2)/(8pi^2)`
- `(8pi^2)/(3rhoL^2)`
- `(3rhoL^3)/(8pi^2)`
- `(8pi^2)/(3rhoL^3)`
Chapter: [0.03] Angular Momentum
Advertisements
The average displacement over a period of S.H.M. is ______.
(A = amplitude of S.H.M.)
0
A
2A
4A
Chapter: [0.04] Oscillations
In which of the following substances, surface tension increases with increase in temperature ?
- Copper
- Molten copper
- Iron
- Molten iron
Chapter: [0.02] Mechanical Properties of Fluids [0.06] Surface Tension
The ratio of diameters of two wires of the same material and length is n : 1. If the same load is applied to both the wires then increases in the length of the thin wire is ........................ (n > 1).
- n1/4 times
- n1/2 times
- n times
- n2 times
Chapter: [0.05] Elasticity
The co-efficient of reflection of an opaque body is 0.16. Its co-efficient of emission is ........................................
- 0.94
- 0.84
- 0.74
- 0.64
Chapter: [0.11] Interference and Diffraction
Let velocity of a sound wave be 'v' and 'ω' be angular velocity. The propagation constant of the wave is .................................
- `sqrt(omega/v)`
- `sqrt(v/omega)`
- `omega/v`
- `v/omega`
Chapter: [0.01] Circular Motion
The value of end correction for an open organ pipe of radius 'r' is .........................
A) 0.3 r
B) 0.6 r
C) 0.9 r
D) 1.2 r
Chapter: [0.06] Superposition of Waves [0.08] Stationary Waves
Distinguish between forced vibrations and resonance.
Chapter: [0.06] Superposition of Waves [0.08] Stationary Waves
Draw neat, labelled diagrams for the modes of vibration of a stretched string in second harmonic and third harmonic.
Chapter: [0.08] Stationary Waves
The area of the upper face of a rectangular block is 0.5 m by 0.5 m and the lower face is fixed. The height of the block is 1 cm. A shearing force applied at the top face produces a displacement of 0.015 mm. Find the strain and shearing force.
(Modulus of rigidity: η = 4.5 x 1010 N/m2)
Chapter: [0.05] Elasticity
Show variation of displacement, velocity, and acceleration with phase for a particle performing linear S.H.M. graphically, when it starts from the extreme position.
Chapter: [0.04] Oscillations
A body starts rotating from rest. Due to a couple of 20 Nm it completes 60 revolutions in one minute. Find the moment of inertia of the body.
Chapter: [0.03] Angular Momentum
In a biprism experiment, a slit is illuminated by a light of wavelength 4800 Å The distance between the slit and biprism is 15 cm and the distance between the biprism and eyepiece is 85 cm. If the distance between virtual sources is 3 mm, determine the distance between 4th bright band on one side and 4th dark band on the other side of the central bright band.
Chapter: [0.11] Interference and Diffraction
Six capacitors of capacities 5, 5. 5, 5, 10 and X μ F are connected as shown in the network in the diagram.
Find :
- The value of X if the network is balanced, and
- The resultant capacitance between A and C.
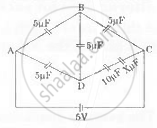
Chapter: [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
Show that the current flowing through a moving coil galvanometer is directly proportional to the angle of deflection of coil.
Chapter: [0.09] Current Electricity [0.14] Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Explain the formation of energy band diagram in case of conductor and semiconductor.
Chapter: [0.19] Semiconductors
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the plane of vibration and plane of polarisation for polarised light.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Theory of Light
Advertisements
State the conditions to get steady interference pattern.
Chapter: [0.11] Interference and Diffraction
In a hydrogen atom, an electron carrying charge 'e' revolves in an orbit of radius 'r' with speed 'v'. Obtain an expression for the magnitude of magnetic moment of a revolving electron.
Chapter: [0.15] Magnetism
Draw a neat, labelled block diagram for a generalised communication system.
Chapter: [0.2] Communication Systems
A red light of wavelength 6400A° in air has wavelength 4000A° in glass. If the wavelength of violet light in air is 4400A°, find its wavelength in glass.
(Assume that μr ≈ μv)
Chapter: [0.11] Interference and Diffraction
The magnetic moment of a magnet of dimensions 5 cm × 2.5 cm × 1.25 cm is 3 Am2. Calculate the intensity of magnetization.
Chapter: [0.11] Magnetic Materials [0.15] Magnetism
An A.C. circuit consists of inductor of inductance 125 mH connected in parallel with a capacitor of capacity 50 μF. Determine the resonant frequency.
Chapter: [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
Calculate the de Broglie wavelength of an electron moving with - of the speed of light in vacuum (Negelct relativistic effect)
(Planck's constant: h = 6.63 x 10-34 Js, Mass of electron : m = 9.11 x 10-28 g)
Chapter: [0.18] Atoms, Molecules and Nuclei
If numerical aperture of a microscope is increased, then its ______.
resolving power decreases
limit of resolution decreases
resolving power remains constant
limit of resolution increases
Chapter: [0.07] Wave Optics
A solenoid of length 1.5 m and 4 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns per metre. A current of 5 A is flowing through it. The magnetic induction at a point inside the solenoid along the axis is ............................. .
(μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am)
- π × 10-5 T
- 2π × 10-5 T
- 3π × 10-5 T
- 4π × 10-5 T
Chapter: [0.12] Electromagnetic Induction [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
Kirchhoff's voltage law and current law are respectively in accordance with the conservation of .................................. .
- charge and momentum
- charge and energy
- energy and charge
- energy and momentum
Chapter: [0.13] Current Electricity
When radiations of wavelength λ1 and λ2 are incident on certain photosensitive, such that E1 > E2 . Then Planck's constant 'h' is ......................... .
(C = Velocity of light).
`((E_1 - E_2)(lambda_1 - lambda_2))/(C(lambda_1 * lambda_2))`
`((E_1 - E_2)lambda_1C)/((lambda_1 - lambda_2)lambda_2)`
`((E_1 - E_2)lambda_1lambda_2)/(C(lambda_2 - lambda_1))`
`((lambda_1 - lambda_2)C)/((E_1 - E_2)lambda_1 * lambda_2)`
Chapter: [0.17] Electrons and Photons
Colour of light emitted by LED depends upon__________________ .
- its forward bias
- its reverse bias
- the band gap of the material of semiconductor
- its size
Chapter: [0.19] Semiconductors
Line of sight propagation is also called as_________________ .
sky wave
ground wave
sound wave
space wave
Chapter: [0.2] Communication Systems
Two parallel plates separated by distance d are kept at potential difference V volt. A charge q of mass m enters in parallel plates with some velocity. The acceleration of the charged particle will be_____________________________ .
- q V/d m
- d m/ q V
- q m/d V
- d V/q m
Chapter: [0.01] Circular Motion
Explain the phenomenon of self induction
Chapter: [0.12] Electromagnetic Induction [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
Explain the phenomenon of mutual induction.
Chapter: [0.12] Electromagnetic Induction [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
Define the coefficient of self-induction.
Chapter: [0.12] Electromagnetic Induction [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
Define coefficient of mutual induction.
Chapter: [0.12] Electromagnetic Induction [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
Write the SI unit and dimention of of co-efficient of self induction
Chapter: [0.12] Electromagnetic Induction [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
A potentiometer wire has a length of 4 m and a resistance of 5 Ω. What resistance should be connected in series with a potentiometer wire and a cell of e.m.f. 2 V having internal resistance 1 Ω to get a potential gradient of 10-3 V/cm ?
Chapter: [0.13] Current Electricity
Derive an expression for the total energy of electron in ‘n' th Bohr orbit. Hence show that energy of the electron is inversely proportional to the square of principal quantum number. Also define binding energy.
Chapter: [0.15] Structure of Atoms and Nuclei [0.18] Atoms, Molecules and Nuclei
The photoelectric threshold wavelength of a metal is 230 nm. Determine the maximum kinetic energy in joule and in eV of the ejects electron for the metal surface when it is exposed to a radiation of wavelength 180 nm.
[Planck’s constant : h = 6.63 * 10-34 Js, Velocity of light : C = 3 * 108 m/s.]
Chapter: [0.17] Electrons and Photons
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
Maharashtra State Board previous year question papers 12th Standard Board Exam Physics with solutions 2013 - 2014
Previous year Question paper for Maharashtra State Board 12th Standard Board Exam -2014 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of Maharashtra State Board 12th Standard Board Exam.
How Maharashtra State Board 12th Standard Board Exam Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
