Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
Solution
| Direct current | Alternating current | ||
| 1 | Direct current flows only in one direction. | 1 | Alternating current reverses its direction periodically with time. |
| 2 | It cannot be used in large-scale generation of electricity for household purposes. | 2 | It is used in household electrical appliances such as electric heater, electric iron, refrigerator etc. |
| 3 | The frequency of direct current is zero. | 3 | The frequency of alternating current in India is 50 Hz. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The magnetic flux through a loop varies according to the relation Φ = 8t2 + 6t + C, where ‘C’ is constant, 'Φ' is in milliweber and 't' is in second. What is the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in the loop at t = 2 seconds.
The magnetic flux through a loop is varying according to a relation `phi = 6t^2 + 7t + 1` where `phi` is in milliweber and t is in second. What is the e.m.f. induced in the loop at t = 2 second?
What is electromagnetic induction?
A circular coil of cross-sectional area 200 cm2 and 20 turns is rotated about the vertical diameter with angular speed of 50 rad s−1 in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 3.0 × 10−2T. Calculate the maximum value of the current in the coil.
Name a common device that uses electromagnets.
Name one device which works on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
Describe one experiment to demonstrate the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
Welders wear special glass goggles while working. Why? Explain.
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
Can a transformer work when it is connected to a D.C. source? Give a reason.
A transformer has 400 turns in the primary winding and 10 turns in the secondary winding. The primary e.m.f. is 250 V and the primary current is 2.0 A. calculate:
(a) The secondary voltage,
(b) The secondary current, assuming 100% efficiency.
Complete the following diagram of a transformer and name the parts labeled A and B. Name the part you have drawn to complete the diagram . What is the material of this part? In this transformer a step-up or step-down? Why?
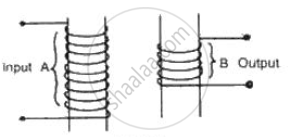
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
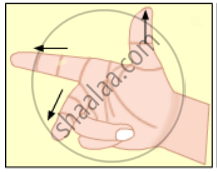
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
Choose the correct option:
A conductor rod of length (l) is moving with velocity (v) in a direction normal to a uniform magnetic field (B). What will be the magnitude of induced emf produced between the ends of the moving conductor?
Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
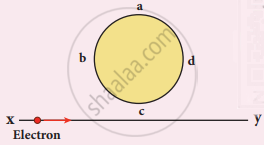
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
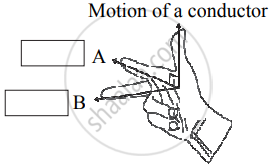
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
A straight metal wire crosses a magnetic field of flux 4 mWb in a time 0.4 s. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the wire.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 4 A. If the magnetic flux through the coil is 6 x 10-5 Wb, find the magnetic energy stored in the medium surrounding the coil.
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
An alternating emf of 0.2 V is applied across an L-C-R series circuit having R = 4Q, C = 80µF, and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is
A cylindrical bar magnet is kept along the axis of a circular coil. If the magnet is rotated about its axis, then ____________.
We can induce the current in a coil by ____________.
For making a strong electromagnet the material of the core should be ______.
Sea turtles return to their birth beach many decades after they were born due to ______.
A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2×10 -3T. Find the force on the conductor.
The working of a dynamo is based on the principle of
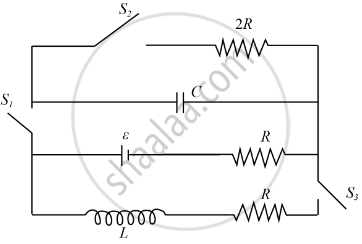
In the given circuit, initially switch S1 is closed and S2 and S3 are open. After charging of capacitor, at t = 0, S1 is open and S2 and S3 are closed. If the relation between inductance capacitance and resistance is L = 4CR2 then the time (in sec) after which current passing through capacitor and inductor will be same is ______ × 10-4 N. (Given R = ℓn(2)mΩ, L = 2mH)
One solenoid is centered inside another. The outer one has a length of 50.0 cm and contains 6750 coils, while the coaxial inner solenoid is 3.0 cm long and π cm2 in area and contains 150 coils. The current in the outer solenoid is changing at 3000 A/s. The emf induced in the inner solenoid is ______ V.
(Round off to two decimal places.)
