Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
उत्तर
| Direct current | Alternating current | ||
| 1 | Direct current flows only in one direction. | 1 | Alternating current reverses its direction periodically with time. |
| 2 | It cannot be used in large-scale generation of electricity for household purposes. | 2 | It is used in household electrical appliances such as electric heater, electric iron, refrigerator etc. |
| 3 | The frequency of direct current is zero. | 3 | The frequency of alternating current in India is 50 Hz. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
Prove theoretically (electromagnetic induction) `e = (dphi)/(dt)`
What condition is necessary for the production of current by electromagnetic induction?
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
Describe different ways to induce current in a coil of wire.
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
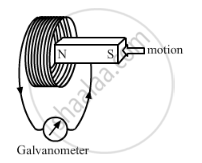
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
When Puja, a student of 10th class, watched her mother washing clothes in the open, she observed coloured soap bubbles and was curious to know why the soap bubbles appear coloured. In the evening when her father, an engineer by profession, came home, she asked him this question. Her father explained to her the basic phenomenon of physics due to which the soap bubbles appear coloured.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Puja and her father?
(b) State the phenomenon of light involved in the formation of coloured soap bubbles.
Welders wear special goggles or face masks with glass windows to protect their eyes from electromagnetic radiations. Name the radiations and write the range of their frequency.
Consider the energy density in a solenoid at its centre and that near its ends. Which of the two is greater?
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
A. C. generator______.
A transformer has 400 turns in the primary winding and 10 turns in the secondary winding. The primary e.m.f. is 250 V and the primary current is 2.0 A. calculate:
(a) The secondary voltage,
(b) The secondary current, assuming 100% efficiency.
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
Choose the correct option:
A conductor rod of length (l) is moving with velocity (v) in a direction normal to a uniform magnetic field (B). What will be the magnitude of induced emf produced between the ends of the moving conductor?
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4 A is ______
Using Ampere's law, obtain an expression for the magnetic induction near a current-carrying straight infinitely long wire.
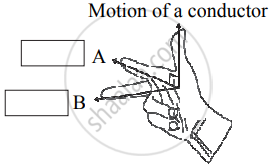
Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
Write the two names in the following diagram.
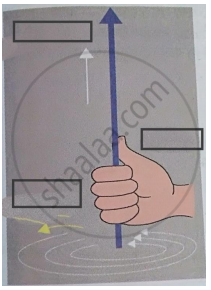
Right hand thumb rule.
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
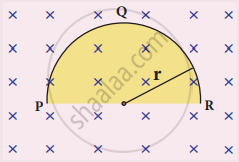
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
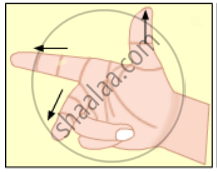
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
Give an illustration of determining direction of induced current by using Lenz’s law.
A straight metal wire crosses a magnetic field of flux 4 mWb in a time 0.4 s. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the wire.
A closely wound circular coil of radius 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field. When the magnetic field is changed from 8000 T to 2000 T in 6 s, an emf of 44 V is induced in it. Calculate the number of turns in the coil.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 0.4 A. If the magnetic flux of 4 mWb is linked with each turn of the coil, find the inductance of the coil.
A layer of atmosphere that reflects medium frequency radio waves which is ineffective during night, is ______.
A metal plate can be heated by ______.
The condition for the praenomen of electromagnetic induction is that there must be a relative motion between ____________.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
Which of the following instruments works by electromagnetic induction?
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
The working of a dynamo is based on the principle of
A rectangular, a square, a circular and an elliptical loop, all in the (x - y) plane, are moving out of a uniform magnetic field with a constant velocity `vecv = vhati`. The magnetic field is directed along the negative z-axis direction. The induced emf, during the passage of these loops, out of the field region, will not remain constant for ______.
A current I = 10 sin(100π t) A is passed in first coil, which induces a maximum e.m.f of 5π volt in second coil. The mutual inductance between the coils is ______.
When an electric current is passed through a wire or a coil, a magnetic field is produced. Is the reverse phenomenon possible i.e, can a magnetic field produce an electric current? Explain with the help of an appropriate example.
