Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
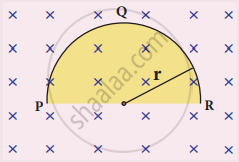
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
विकल्प
Zero
`("Bv"pi"r"^2)/2` and P is at higher potential
πrBv and R is at higher potential
2rBv and R is at higher potential
उत्तर
2rBv and R is at higher potential
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
A metal rod `1/sqrtpi `m long rotates about one of its ends perpendicular to a plane whose magnetic induction is 4 x 10-3 T. Calculate the number of revolutions made by the rod per second if the e.m.f. induced between the ends of the rod is 16 mV.
Explain why, an electromagnet is called a temporary magnet.
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
A metal plate can be heated by ______.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
