Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4 A is ______
विकल्प
0.4 J
0.1 J
0.04 J
0.01 J
उत्तर
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4 A is 0.4 J.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loud speaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area 2 cm2 with 25 closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the field region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick 90° turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in the coil (measured by a ballistic galvanometer connected to coil) is 7.5 mC. The combined resistance of the coil and the galvanometer is 0.50 Ω. Estimate the field strength of magnet.
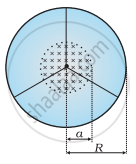
A line charge λ per unit length is lodged uniformly onto the rim of a wheel of mass M and radius R. The wheel has light non-conducting spokes and is free to rotate without friction about its axis (Figure). A uniform magnetic field extends over a circular region within the rim. It is given by,
B = − B0 k (r ≤ a; a < R)
= 0 (otherwise)
What is the angular velocity of the wheel after the field is suddenly switched off?
If ‘R’ is the radius of dees and ‘B’ be the magnetic field of induction in which positive charges (q) of mass (m) escape from the cyclotron, then its maximum speed (vmax) is _______.
A) `(qR)/(Bm)`
B)`(qm)/(Br)`
C) `(qBR)/m`
D) `m/(qBR)`
Name a common device that uses electromagnets.
When an electric current is passed through any wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. Then why an electric iron connecting cable does not attract nearby iron objects when electric current switched on through it?
Explain why, the core of an electromagnet should be of soft iron and not of steel.
The north-south polarities of an electromagnet can be found easily by using:
(a) Fleming's right-hand rule
(b) Fleming's left-hand rule
(c) Clock face rule
(d) Left-hand thumb rule
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be:
(a) north pole
(b) east pole
(c) south pole
(d) west pole
What condition is necessary for the production of current by electromagnetic induction?
Describe different ways to induce current in a coil of wire.
An induced current is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil. The magnitude of induced current does not depend on:
(a) the speed with which the magnet is moved
(b) the number of turns of the coil
(c) the resistivity of the wire of the coil
(d) the strength of the magnet
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A loop of wire is held near a magnet.
Welders wear special goggles or face masks with glass windows to protect their eyes from electromagnetic radiations. Name the radiations and write the range of their frequency.
A light metal disc on the top of an electromagnet is thrown up as the current is switched on. Why? Give reason.
Consider the energy density in a solenoid at its centre and that near its ends. Which of the two is greater?
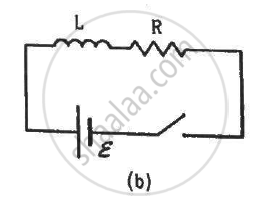
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
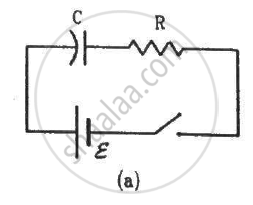
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-up transformer.
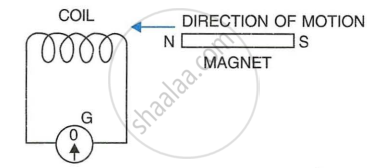
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
Draw and label the diagram of a simple D.C. motor.
(a) Explain the rotation of the coil, giving a reason for your answer.
(b) How can you reverse the direction of rotation of the armature?
(c) How can you increase the speed of rotation of the motor?
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
The diagram shows a rectangular coil ABCD, suspended freely between the concave pole pieces of a permanent horseshoe magnet, such that the plane of the coil is parallel to the magnetic field.

(i) State your observation, when current is switched on.
(ii) Give an explanation for your observation in (i).
(iii) State the rule, which will help you to find the motion of rotation of coil.
(iv) In which position will the coil ultimately come to rest?
(v) State four ways of increasing the magnitude of force acting on the coil.
Choose the correct option:
A conductor rod of length (l) is moving with velocity (v) in a direction normal to a uniform magnetic field (B). What will be the magnitude of induced emf produced between the ends of the moving conductor?
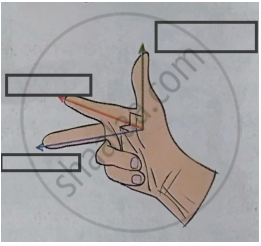
Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
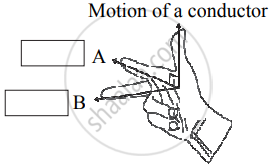
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
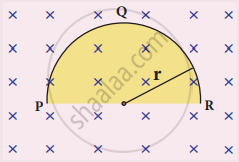
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
What for an inductor is used? Give some examples.
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
The magnetic flux passing through a coil perpendicular to its plane is a function of time and is given by OB = (2t3 + 4t2 + 8t + 8) Wb. If the resistance of the coil is 5 Ω, determine the induced current through the coil at a time t = 3 second.
An alternating emf of 0.2 V is applied across an L-C-R series circuit having R = 4Q, C = 80µF, and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is
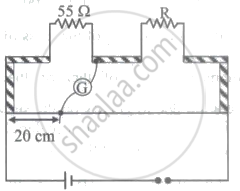
Shown in the figure below is a metre bridge set up with null deflection in the galvanometer. The value of the unknown resistance R is ______
A layer of atmosphere that reflects medium frequency radio waves which is ineffective during night, is ______.
A cylindrical bar magnet (A) and similar unmagnetized cylindrical iron bar (B) are dropped through metallic pipe. The time taken to come down by ____________.
There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then ______.
The instrument that use to defect electric current in the circuit is known as ____________.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
What will be observed when the Magnet starts oscillating through the coil. Explain the reason behind this observation.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
A coil of one turn is made of a wire of certain length and then from the same length, a coil of two turns is made. If the same current is passed in both the cases, then the ratio of the magnetic inductions at their centres will be:
Which of the following phenomena makes use of electromagnetic induction?
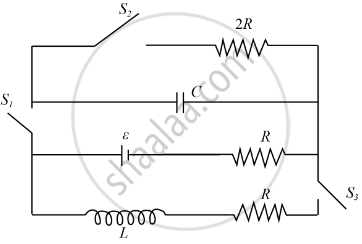
In the given circuit, initially switch S1 is closed and S2 and S3 are open. After charging of capacitor, at t = 0, S1 is open and S2 and S3 are closed. If the relation between inductance capacitance and resistance is L = 4CR2 then the time (in sec) after which current passing through capacitor and inductor will be same is ______ × 10-4 N. (Given R = ℓn(2)mΩ, L = 2mH)
A current I = 10 sin(100π t) A is passed in first coil, which induces a maximum e.m.f of 5π volt in second coil. The mutual inductance between the coils is ______.
An expression for oscillating electric field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given as Ez = 300 sin(5π × 103x - 3π × 1011t)Vm-1 Then, the value of magnetic field amplitude will be ______. (Given: speed of light in Vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
Which type of force is experienced by a moving charge in a magnetic field?
When an electric current is passed through a wire or a coil, a magnetic field is produced. Is the reverse phenomenon possible i.e, can a magnetic field produce an electric current? Explain with the help of an appropriate example.
