Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
उत्तर
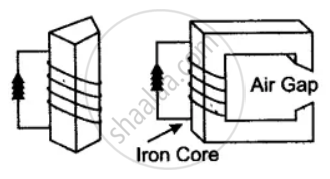
The electromagnet is a temporary magnet which can be magnetized or demagnetized in a very short time as per our requirements. In the simplest form, an electromagnet consists simply of a soft iron core around which a large number of turns of insulated wire are wound. Two of the simple forms of an electro magnet are shown in the figure alongside.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A solenoid of length 1.5 m and 4 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns per metre. A current of 5 A is flowing through it. The magnetic induction at a point inside the solenoid along the axis is ............................. .
(μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am)
- π × 10-5 T
- 2π × 10-5 T
- 3π × 10-5 T
- 4π × 10-5 T
When an electric current is passed through any wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. Then why an electric iron connecting cable does not attract nearby iron objects when electric current switched on through it?
State three ways in which the strength of an electromagnet can be increased.
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
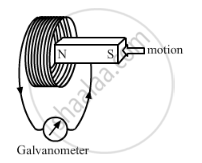
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
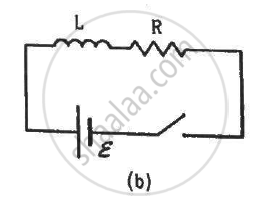
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
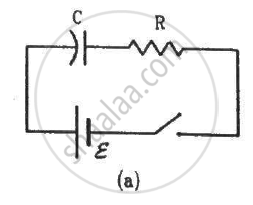
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
A conducting square loop having edges of length 2.0 cm is rotated through 180° about a diagonal in 0.20 s. A magnetic field B exists in the region which is perpendicular to the loop in its initial position. If the average induced emf during the rotation is 20 mV, find the magnitude of the magnetic field.
Choose the correct option:
A conductor rod of length (l) is moving with velocity (v) in a direction normal to a uniform magnetic field (B). What will be the magnitude of induced emf produced between the ends of the moving conductor?
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 0.4 A. If the magnetic flux of 4 mWb is linked with each turn of the coil, find the inductance of the coil.
The condition for the praenomen of electromagnetic induction is that there must be a relative motion between ____________.
Which type of force is experienced by a moving charge in a magnetic field?
