Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4 A is ______
Options
0.4 J
0.1 J
0.04 J
0.01 J
Solution
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4 A is 0.4 J.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Electric field intensity in free space at a distance ‘r’ outside the charged conducting sphere of radius ‘R’ in terms of surface charge density ‘ a ’ is............................
(a)`sigma / in_0[R/r]^2`
(b)`in_0/sigma[R/r]^2`
(c)`R/r[sigma/in_0]^2`
(d)`R/sigma[r/in_0]^2`
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
A metal rod `1/sqrtpi `m long rotates about one of its ends perpendicular to a plane whose magnetic induction is 4 x 10-3 T. Calculate the number of revolutions made by the rod per second if the e.m.f. induced between the ends of the rod is 16 mV.
When a bar magnet is pushed towards (or away) from the coil connected to a galvanometer, the pointer in the galvanometer deflects. Identify the phenomenon causing this deflection and write the factors on which the amount and direction of the deflection depends. State the laws describing this phenomenon.
Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
What is electromagnetic induction?
An emf of 2V is induced in a coil when the current in it is changed from 0A to 10A in 0·40 sec. Find the coefficient of self-inductance of the coil.
When an electric current is passed through any wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. Then why an electric iron connecting cable does not attract nearby iron objects when electric current switched on through it?
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
What is an electromagnet? Describe the construction and working of an electromagnet with the help of a labelled diagram.
Name one device which works on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
An induced current is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil. The magnitude of induced current does not depend on:
(a) the speed with which the magnet is moved
(b) the number of turns of the coil
(c) the resistivity of the wire of the coil
(d) the strength of the magnet
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
The current is stopped in a wire held near a loop of wire .
A light metal disc on the top of an electromagnet is thrown up as the current is switched on. Why? Give reason.
Show diagrammatically how an alternating emf is generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rotating loop.
Consider the energy density in a solenoid at its centre and that near its ends. Which of the two is greater?
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
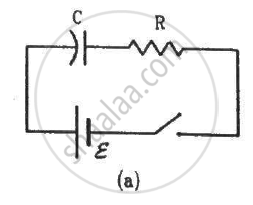
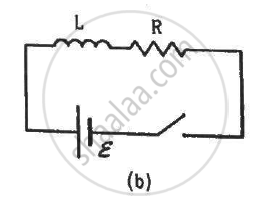
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
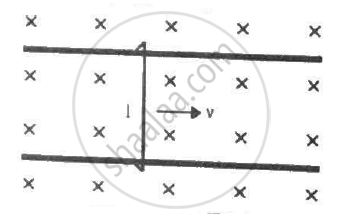
Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation l. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
The diagram 10 shows two coils X and Y. The coil X is connected to a battery S and a key K. The coil Y is connected to a galvanometer G.
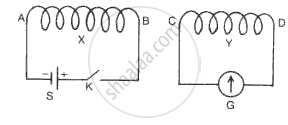
When the key K is closed. State the polarity
(i)At the end of the coil X,
(ii)At the end C of the coil Y,
(iii)At the end C of the coil Y if the coil Y is (a) Moved towards the coil X, (b) Moved away from the coil X.
Fig. shows a simple form of an A.C. generator.

(a) Name the parts labeled A and B.
(b) What would be the effect of doubling the number of turns on the coil if the speed of rotation remains unchanged?
(c) Which of the output terminals is positive if the coil is rotating in the
direction shown in the diagram (anticlockwise)?
( d ) What is the position of the rotating coil when p.d. across its ends is zero? Explain why p.d. is zero when the coil is at this position .
(e) Sketch a graph showing how the p.d. across the ends of the rotating coil varies with time for an A.C. dynamo.
( f) On th e same sheet of paper and vertically below the first graph using the same time scale, sketch graphs to show the effect of
(i) Doubling the speed of rotation and at the same time keeping
the field and the number of turns constant,
(ii ) Doubling the number of turns on the coil and at the same time
doubling the speed of rotation of the coil, keeping th e speed
constant.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
You have been provided with a solenoid AB.
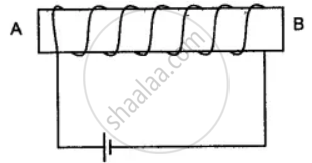
(i) What is the polarity at end A?
(ii) Give one advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
Choose the correct option:
A conductor rod of length (l) is moving with velocity (v) in a direction normal to a uniform magnetic field (B). What will be the magnitude of induced emf produced between the ends of the moving conductor?
Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
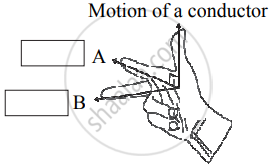
Write Fleming’s right hand thumb rule with the help of diagram.
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Right hand thumb rule.
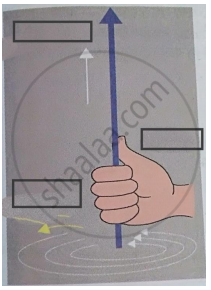
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
The magnetic flux passing through a coil perpendicular to its plane is a function of time and is given by OB = (2t3 + 4t2 + 8t + 8) Wb. If the resistance of the coil is 5 Ω, determine the induced current through the coil at a time t = 3 second.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 4 A. If the magnetic flux through the coil is 6 x 10-5 Wb, find the magnetic energy stored in the medium surrounding the coil.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 0.4 A. If the magnetic flux of 4 mWb is linked with each turn of the coil, find the inductance of the coil.
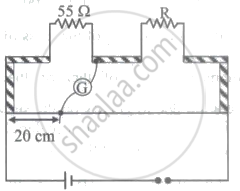
Shown in the figure below is a metre bridge set up with null deflection in the galvanometer. The value of the unknown resistance R is ______
A layer of atmosphere that reflects medium frequency radio waves which is ineffective during night, is ______.
A generator has an e.m.f. of 440 Volt and internal resistance of 4000 hm. Its terminals are connected to a load of 4000 ohm. The voltage across the load is ______.
There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then ______.
A metal plate can be heated by ______.
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
Induced current flows through a coil ______.
A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
A coil of one turn is made of a wire of certain length and then from the same length, a coil of two turns is made. If the same current is passed in both the cases, then the ratio of the magnetic inductions at their centres will be:
A rectangular, a square, a circular and an elliptical loop, all in the (x - y) plane, are moving out of a uniform magnetic field with a constant velocity `vecv = vhati`. The magnetic field is directed along the negative z-axis direction. The induced emf, during the passage of these loops, out of the field region, will not remain constant for ______.
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
A conducting bar of length L is free to slide on two parallel conducting rails as shown in the figure
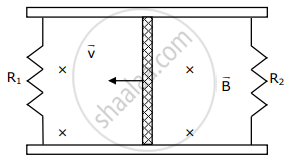
Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected across the ends of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` pointing into the page. An external agent pulls the bar to the left at a constant speed v. The correct statement about the directions of induced currents I1 and I2 flowing through R1 and R2 respectively is:
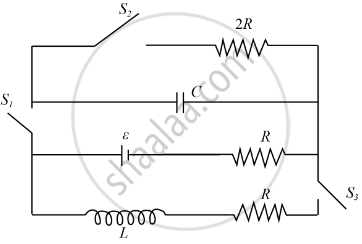
In the given circuit, initially switch S1 is closed and S2 and S3 are open. After charging of capacitor, at t = 0, S1 is open and S2 and S3 are closed. If the relation between inductance capacitance and resistance is L = 4CR2 then the time (in sec) after which current passing through capacitor and inductor will be same is ______ × 10-4 N. (Given R = ℓn(2)mΩ, L = 2mH)
The charge will flow through a galvanometer of resistance 200Ω connected to a 400Ω circular coil of 1000 turns wound on a wooden stick 20 mm in diameter, if a magnetic field B = 0.012 T parallel to the axis of the stick decreased suddenly to zero, is near ______.
Which type of force is experienced by a moving charge in a magnetic field?
When an electric current is passed through a wire or a coil, a magnetic field is produced. Is the reverse phenomenon possible i.e, can a magnetic field produce an electric current? Explain with the help of an appropriate example.
