Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is an electromagnet? Describe the construction and working of an electromagnet with the help of a labelled diagram.
Solution
Electromagnet:
It is a magnet that works on the principle of magnetic effect of current.
A temporary magnet consisting of a long coil of insulated copper wire wrapped around a soft iron core is called an electromagnet.
Construction and working:

We take a rod NS of soft iron and wind coil C of insulated copper wire around it. When we connect the two ends of the copper coil to a battery, an electromagnet is formed. The iron rod inside the coil becomes a strong electromagnet on passing a current. The magnetic field produced by an electromagnet is very strong.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loud speaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area 2 cm2 with 25 closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the field region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick 90° turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in the coil (measured by a ballistic galvanometer connected to coil) is 7.5 mC. The combined resistance of the coil and the galvanometer is 0.50 Ω. Estimate the field strength of magnet.
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
Name and state the law which determines the direction of induced current.
or
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4 A is ______
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
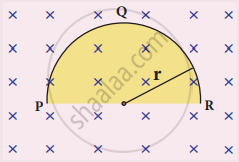
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
A conducting bar of length L is free to slide on two parallel conducting rails as shown in the figure
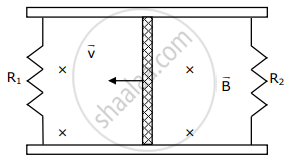
Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected across the ends of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` pointing into the page. An external agent pulls the bar to the left at a constant speed v. The correct statement about the directions of induced currents I1 and I2 flowing through R1 and R2 respectively is:
