Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If ‘R’ is the radius of dees and ‘B’ be the magnetic field of induction in which positive charges (q) of mass (m) escape from the cyclotron, then its maximum speed (vmax) is _______.
A) `(qR)/(Bm)`
B)`(qm)/(Br)`
C) `(qBR)/m`
D) `m/(qBR)`
उत्तर
`(qBR)/m`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Electric field intensity in free space at a distance ‘r’ outside the charged conducting sphere of radius ‘R’ in terms of surface charge density ‘ a ’ is............................
(a)`sigma / in_0[R/r]^2`
(b)`in_0/sigma[R/r]^2`
(c)`R/r[sigma/in_0]^2`
(d)`R/sigma[r/in_0]^2`
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
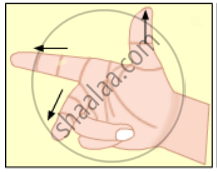
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
What is electromagnetic induction?
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
What is an electromagnet? Describe the construction and working of an electromagnet with the help of a labelled diagram.
Explain why, an electromagnet is called a temporary magnet.
State the factors on which the strength of an electromagnet depends. How does it depend on these factors?
The north-south polarities of an electromagnet can be found easily by using:
(a) Fleming's right-hand rule
(b) Fleming's left-hand rule
(c) Clock face rule
(d) Left-hand thumb rule
The most suitable material for making the core of an electromagnet is:
(a) soft iron
(b) brass
(c) aluminium
(d) steel
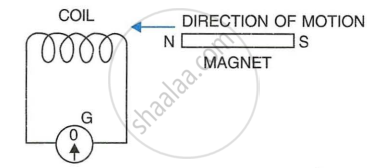
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
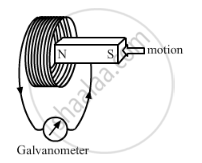
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
Name and state the law which determines the direction of induced current.
or
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
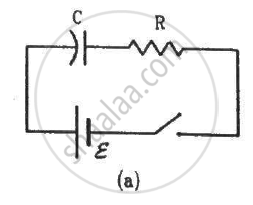
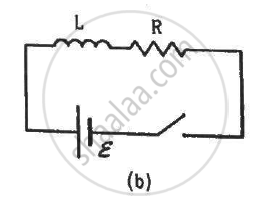
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-up transformer.
The diagram 10 shows two coils X and Y. The coil X is connected to a battery S and a key K. The coil Y is connected to a galvanometer G.
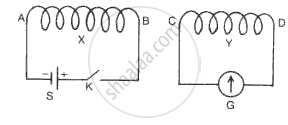
When the key K is closed. State the polarity
(i)At the end of the coil X,
(ii)At the end C of the coil Y,
(iii)At the end C of the coil Y if the coil Y is (a) Moved towards the coil X, (b) Moved away from the coil X.
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
A. C. generator______.
A transformer has 400 turns in the primary winding and 10 turns in the secondary winding. The primary e.m.f. is 250 V and the primary current is 2.0 A. calculate:
(a) The secondary voltage,
(b) The secondary current, assuming 100% efficiency.
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
List some of the practical applications of an electromagnet.
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4 A is ______
Using Ampere's law, obtain an expression for the magnetic induction near a current-carrying straight infinitely long wire.
Write Fleming’s right hand thumb rule with the help of diagram.
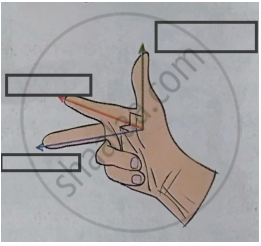
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
Show that Lenz’s law is in accordance with the law of conservation of energy.
A closely wound circular coil of radius 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field. When the magnetic field is changed from 8000 T to 2000 T in 6 s, an emf of 44 V is induced in it. Calculate the number of turns in the coil.
An alternating emf of 0.2 V is applied across an L-C-R series circuit having R = 4Q, C = 80µF, and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is
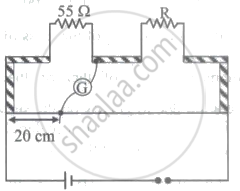
Shown in the figure below is a metre bridge set up with null deflection in the galvanometer. The value of the unknown resistance R is ______
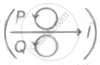
Metal rings P and Q are lying in the same plane, where current I is increasing steadily. The induced current in metal rings is shown correctly in figure.
A cylindrical bar magnet is kept along the axis of a circular coil. If the magnet is rotated about its axis, then ____________.
A cylindrical bar magnet (A) and similar unmagnetized cylindrical iron bar (B) are dropped through metallic pipe. The time taken to come down by ____________.
There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then ______.
The instrument that use to defect electric current in the circuit is known as ____________.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
Name some equipment that uses electromagnetism for functioning.
Induced current flows through a coil ______.
For making a strong electromagnet the material of the core should be ______.
Sea turtles return to their birth beach many decades after they were born due to ______.
A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
A coil of one turn is made of a wire of certain length and then from the same length, a coil of two turns is made. If the same current is passed in both the cases, then the ratio of the magnetic inductions at their centres will be:
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
A rectangular, a square, a circular and an elliptical loop, all in the (x - y) plane, are moving out of a uniform magnetic field with a constant velocity `vecv = vhati`. The magnetic field is directed along the negative z-axis direction. The induced emf, during the passage of these loops, out of the field region, will not remain constant for ______.
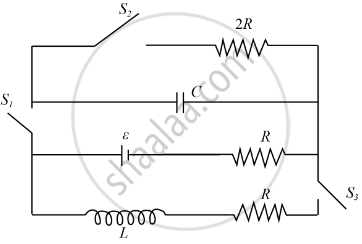
In the given circuit, initially switch S1 is closed and S2 and S3 are open. After charging of capacitor, at t = 0, S1 is open and S2 and S3 are closed. If the relation between inductance capacitance and resistance is L = 4CR2 then the time (in sec) after which current passing through capacitor and inductor will be same is ______ × 10-4 N. (Given R = ℓn(2)mΩ, L = 2mH)
An expression for oscillating electric field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given as Ez = 300 sin(5π × 103x - 3π × 1011t)Vm-1 Then, the value of magnetic field amplitude will be ______. (Given: speed of light in Vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
