Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
उत्तर
Fleming’s right-hand rule:-
Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of the right hand so that they are perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger indicates the direction of the magnetic field and the thumb shows the direction of motion of the conductor, then the middle finger will show the direction of the induced current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
The magnetic flux through a loop is varying according to a relation `phi = 6t^2 + 7t + 1` where `phi` is in milliweber and t is in second. What is the e.m.f. induced in the loop at t = 2 second?
A circular coil of cross-sectional area 200 cm2 and 20 turns is rotated about the vertical diameter with angular speed of 50 rad s−1 in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 3.0 × 10−2T. Calculate the maximum value of the current in the coil.
Name a common device that uses electromagnets.
State three ways in which the strength of an electromagnet can be increased.
Name two devices in which electromagnets are used and two devices where permanent magnets are used.
What is an electromagnet? Describe the construction and working of an electromagnet with the help of a labelled diagram.
When current is 'switched on' and 'switched off' in a coil, a current is induced in another coil kept near it. What is this phenomenon known as?
Describe different ways to induce current in a coil of wire.
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
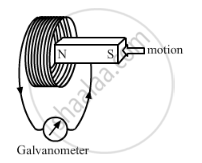
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
Name and state the law which determines the direction of induced current.
or
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
The coil of a moving-coil galvanometer keeps on oscillating for a long time if it is deflected and released. If the ends of the coil are connected together, the oscillation stops at once. Explain.
L, C and R represent the physical quantities inductance, capacitance and resistance respectively. Which of the following combinations have dimensions of frequency?
(a) `1/(RC)`
(b) `R/L`
(c) `1/sqrt(LC)`
(d) C/L
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
Draw a labelled diagram to show how an electromagnet is made.
Fleming's left hand rule : electric current : : Fleming's right hand rule : _______
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
Show that Lenz’s law is in accordance with the law of conservation of energy.
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
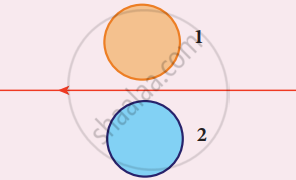
Metal rings P and Q are lying in the same plane, where current I is increasing steadily. The induced current in metal rings is shown correctly in figure.
A layer of atmosphere that reflects medium frequency radio waves which is ineffective during night, is ______.
A cylindrical bar magnet (A) and similar unmagnetized cylindrical iron bar (B) are dropped through metallic pipe. The time taken to come down by ____________.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
A coil of one turn is made of a wire of certain length and then from the same length, a coil of two turns is made. If the same current is passed in both the cases, then the ratio of the magnetic inductions at their centres will be:
A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2×10 -3T. Find the force on the conductor.
The working of a dynamo is based on the principle of
Which of the following phenomena makes use of electromagnetic induction?
A conducting bar of length L is free to slide on two parallel conducting rails as shown in the figure
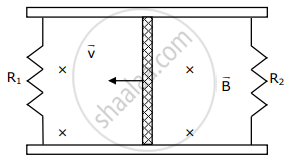
Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected across the ends of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` pointing into the page. An external agent pulls the bar to the left at a constant speed v. The correct statement about the directions of induced currents I1 and I2 flowing through R1 and R2 respectively is:
An expression for oscillating electric field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given as Ez = 300 sin(5π × 103x - 3π × 1011t)Vm-1 Then, the value of magnetic field amplitude will be ______. (Given: speed of light in Vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
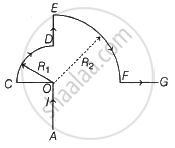
In the current carrying conductor (AOCDEFG) as shown, the magnetic induction at point O is ______.
(R1 and R2 are radii of CD and EF respectively. l = current in the loop, μ0 = permeability of free space)
Which type of force is experienced by a moving charge in a magnetic field?
