Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The coil of a moving-coil galvanometer keeps on oscillating for a long time if it is deflected and released. If the ends of the coil are connected together, the oscillation stops at once. Explain.
उत्तर
When the ends of the coil are not connected, the coil acts as an inductor in which oscillations persist until the current decays slowly. When these ends are connected, the coil forms a close loop; hence, there is inductance across the ends and the coil does not behave like an inductor. Therefore, all oscillations stop at once.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The magnetic flux through a loop varies according to the relation Φ = 8t2 + 6t + C, where ‘C’ is constant, 'Φ' is in milliweber and 't' is in second. What is the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in the loop at t = 2 seconds.
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loud speaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area 2 cm2 with 25 closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the field region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick 90° turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in the coil (measured by a ballistic galvanometer connected to coil) is 7.5 mC. The combined resistance of the coil and the galvanometer is 0.50 Ω. Estimate the field strength of magnet.
A circular coil of cross-sectional area 200 cm2 and 20 turns is rotated about the vertical diameter with angular speed of 50 rad s−1 in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 3.0 × 10−2T. Calculate the maximum value of the current in the coil.
Name a common device that uses electromagnets.
When an electric current is passed through any wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. Then why an electric iron connecting cable does not attract nearby iron objects when electric current switched on through it?
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
An induced current is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil. The magnitude of induced current does not depend on:
(a) the speed with which the magnet is moved
(b) the number of turns of the coil
(c) the resistivity of the wire of the coil
(d) the strength of the magnet
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-down transformer.
Draw and label the diagram of a simple D.C. motor.
(a) Explain the rotation of the coil, giving a reason for your answer.
(b) How can you reverse the direction of rotation of the armature?
(c) How can you increase the speed of rotation of the motor?
Draw a labelled diagram to show how an electromagnet is made.
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
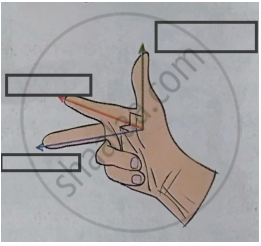
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
A straight metal wire crosses a magnetic field of flux 4 mWb in a time 0.4 s. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the wire.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
A coil of one turn is made of a wire of certain length and then from the same length, a coil of two turns is made. If the same current is passed in both the cases, then the ratio of the magnetic inductions at their centres will be:
