Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The coil of a moving-coil galvanometer keeps on oscillating for a long time if it is deflected and released. If the ends of the coil are connected together, the oscillation stops at once. Explain.
Solution
When the ends of the coil are not connected, the coil acts as an inductor in which oscillations persist until the current decays slowly. When these ends are connected, the coil forms a close loop; hence, there is inductance across the ends and the coil does not behave like an inductor. Therefore, all oscillations stop at once.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A solenoid of length 1.5 m and 4 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns per metre. A current of 5 A is flowing through it. The magnetic induction at a point inside the solenoid along the axis is ............................. .
(μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am)
- π × 10-5 T
- 2π × 10-5 T
- 3π × 10-5 T
- 4π × 10-5 T
When a bar magnet is pushed towards (or away) from the coil connected to a galvanometer, the pointer in the galvanometer deflects. Identify the phenomenon causing this deflection and write the factors on which the amount and direction of the deflection depends. State the laws describing this phenomenon.
What is electromagnetic induction?
Name a common device that uses electromagnets.
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A motor works on the principle electric generator?
Describe one experiment to demonstrate the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
Show diagrammatically how an alternating emf is generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rotating loop.
Consider the energy density in a solenoid at its centre and that near its ends. Which of the two is greater?
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
Draw a labelled diagram to show how an electromagnet is made.
State the condition at which we say the two coils kept close to each other are perfectly coupled with each other.
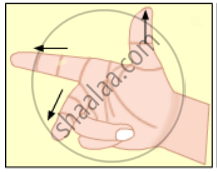
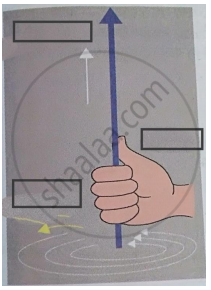
Write Fleming’s right hand thumb rule with the help of diagram.
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Right hand thumb rule.
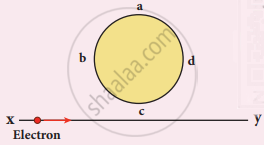
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
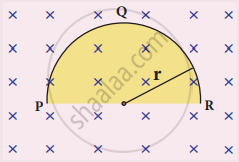
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
What for an inductor is used? Give some examples.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
A metal plate can be heated by ______.
Which of the following phenomena makes use of electromagnetic induction?
