Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the condition at which we say the two coils kept close to each other are perfectly coupled with each other.
Solution
When the coefficient of coupling (K) is 1, then the two coils kept close to each other are said to be perfectly coupled with each other.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
Prove theoretically (electromagnetic induction) `e = (dphi)/(dt)`
State the factors on which the strength of an electromagnet depends. How does it depend on these factors?
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be:
(a) north pole
(b) east pole
(c) south pole
(d) west pole
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
When current is 'switched on' and 'switched off' in a coil, a current is induced in another coil kept near it. What is this phenomenon known as?
Name one device which works on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
An induced current is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil. The magnitude of induced current does not depend on:
(a) the speed with which the magnet is moved
(b) the number of turns of the coil
(c) the resistivity of the wire of the coil
(d) the strength of the magnet
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
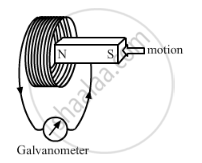
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A magnet is moved through a loop of wire .
Welders wear special glass goggles while working. Why? Explain.
When Puja, a student of 10th class, watched her mother washing clothes in the open, she observed coloured soap bubbles and was curious to know why the soap bubbles appear coloured. In the evening when her father, an engineer by profession, came home, she asked him this question. Her father explained to her the basic phenomenon of physics due to which the soap bubbles appear coloured.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Puja and her father?
(b) State the phenomenon of light involved in the formation of coloured soap bubbles.
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
The coil of a moving-coil galvanometer keeps on oscillating for a long time if it is deflected and released. If the ends of the coil are connected together, the oscillation stops at once. Explain.
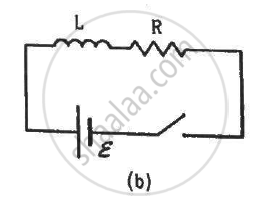
The switches in figure (a) and (b) are closed at t = 0 and reopened after a long time at t = t0.
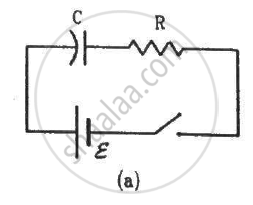
(a) The charge on C just after t = 0 is εC.
(b) The charge on C long after t = 0 is εC.
(c) The current in L just before t = t0 is ε/R.
(d) The current in L long after t = t0 is ε/R.
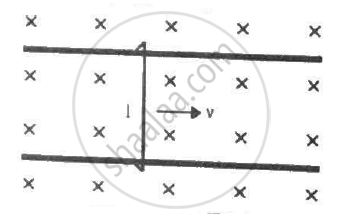
Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation l. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
D.C. motor ______.
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
Draw a labelled diagram to make an electromagnet from a soft iron bar. Mark the polarity at its ends in your diagram. What precaution would you observe while making it?
The diagram shows a rectangular coil ABCD, suspended freely between the concave pole pieces of a permanent horseshoe magnet, such that the plane of the coil is parallel to the magnetic field.

(i) State your observation, when current is switched on.
(ii) Give an explanation for your observation in (i).
(iii) State the rule, which will help you to find the motion of rotation of coil.
(iv) In which position will the coil ultimately come to rest?
(v) State four ways of increasing the magnitude of force acting on the coil.
The right-hand thumb rule is also called _______ rule.
Which of the following scientist invented the rule of electromagnetic induction?
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
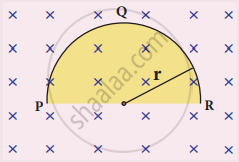
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
State Lenz’s law.
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 4 A. If the magnetic flux through the coil is 6 x 10-5 Wb, find the magnetic energy stored in the medium surrounding the coil.
An alternating emf of 0.2 V is applied across an L-C-R series circuit having R = 4Q, C = 80µF, and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is
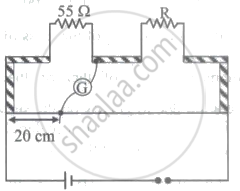
Shown in the figure below is a metre bridge set up with null deflection in the galvanometer. The value of the unknown resistance R is ______
A cylindrical bar magnet is kept along the axis of a circular coil. If the magnet is rotated about its axis, then ____________.
There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then ______.
The condition for the praenomen of electromagnetic induction is that there must be a relative motion between ____________.
We can induce the current in a coil by ____________.
What should be the core of an electromagnet?
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
Which of the following instruments works by electromagnetic induction?
Sea turtles return to their birth beach many decades after they were born due to ______.
An expression for oscillating electric field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given as Ez = 300 sin(5π × 103x - 3π × 1011t)Vm-1 Then, the value of magnetic field amplitude will be ______. (Given: speed of light in Vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
The primary of a transformer has 400 turns while the secondary has 2000 turns. If the power output from the secondary at 1000 Vis 12 kW, what is the primary voltage?
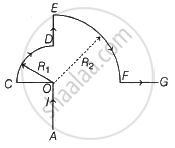
In the current carrying conductor (AOCDEFG) as shown, the magnetic induction at point O is ______.
(R1 and R2 are radii of CD and EF respectively. l = current in the loop, μ0 = permeability of free space)
When an electric current is passed through a wire or a coil, a magnetic field is produced. Is the reverse phenomenon possible i.e, can a magnetic field produce an electric current? Explain with the help of an appropriate example.
