Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
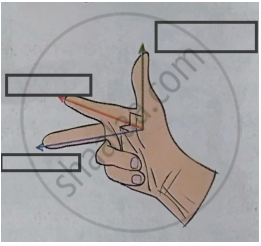
Solution

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
A metal rod `1/sqrtpi `m long rotates about one of its ends perpendicular to a plane whose magnetic induction is 4 x 10-3 T. Calculate the number of revolutions made by the rod per second if the e.m.f. induced between the ends of the rod is 16 mV.
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
Prove theoretically (electromagnetic induction) `e = (dphi)/(dt)`
If ‘R’ is the radius of dees and ‘B’ be the magnetic field of induction in which positive charges (q) of mass (m) escape from the cyclotron, then its maximum speed (vmax) is _______.
A) `(qR)/(Bm)`
B)`(qm)/(Br)`
C) `(qBR)/m`
D) `m/(qBR)`
An emf of 2V is induced in a coil when the current in it is changed from 0A to 10A in 0·40 sec. Find the coefficient of self-inductance of the coil.
Explain why, an electromagnet is called a temporary magnet.
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
Describe one experiment to demonstrate the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
Show diagrammatically how an alternating emf is generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rotating loop.
Figure shows a long U-shaped wire of width l placed in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A wire of length l is slid on the U-shaped wire with a constant velocity v towards right. The resistance of all the wires is r per unit length. At t = 0, the sliding wire is close to the left edge of the U-shaped wire. (a) Calculate the force needed to keep the sliding wire moving with a constant velocity v. (b) If the force needed just after t = 0 is F0, find the time at which the force needed will be F0/2.0
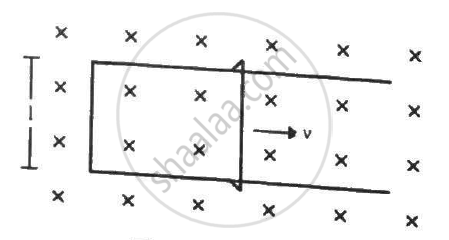
Can a transformer work when it is connected to a D.C. source? Give a reason.
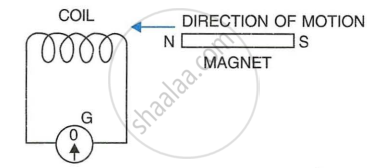
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
Draw and label the diagram of a simple D.C. motor.
(a) Explain the rotation of the coil, giving a reason for your answer.
(b) How can you reverse the direction of rotation of the armature?
(c) How can you increase the speed of rotation of the motor?
Fig. shows a simple form of an A.C. generator.

(a) Name the parts labeled A and B.
(b) What would be the effect of doubling the number of turns on the coil if the speed of rotation remains unchanged?
(c) Which of the output terminals is positive if the coil is rotating in the
direction shown in the diagram (anticlockwise)?
( d ) What is the position of the rotating coil when p.d. across its ends is zero? Explain why p.d. is zero when the coil is at this position .
(e) Sketch a graph showing how the p.d. across the ends of the rotating coil varies with time for an A.C. dynamo.
( f) On th e same sheet of paper and vertically below the first graph using the same time scale, sketch graphs to show the effect of
(i) Doubling the speed of rotation and at the same time keeping
the field and the number of turns constant,
(ii ) Doubling the number of turns on the coil and at the same time
doubling the speed of rotation of the coil, keeping th e speed
constant.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
A. C. generator______.
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
What is an electromagnet? List any two uses.
The right-hand thumb rule is also called _______ rule.
Which of the following scientist invented the rule of electromagnetic induction?
A straight metal wire crosses a magnetic field of flux 4 mWb in a time 0.4 s. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the wire.
The magnetic flux passing through a coil perpendicular to its plane is a function of time and is given by OB = (2t3 + 4t2 + 8t + 8) Wb. If the resistance of the coil is 5 Ω, determine the induced current through the coil at a time t = 3 second.
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 0.4 A. If the magnetic flux of 4 mWb is linked with each turn of the coil, find the inductance of the coil.
A cylindrical bar magnet (A) and similar unmagnetized cylindrical iron bar (B) are dropped through metallic pipe. The time taken to come down by ____________.
The instrument that use to defect electric current in the circuit is known as ____________.
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
Induced current flows through a coil ______.
For making a strong electromagnet the material of the core should be ______.
A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
Which of the following phenomena makes use of electromagnetic induction?
A rectangular, a square, a circular and an elliptical loop, all in the (x - y) plane, are moving out of a uniform magnetic field with a constant velocity `vecv = vhati`. The magnetic field is directed along the negative z-axis direction. The induced emf, during the passage of these loops, out of the field region, will not remain constant for ______.
Which type of force is experienced by a moving charge in a magnetic field?
When an electric current is passed through a wire or a coil, a magnetic field is produced. Is the reverse phenomenon possible i.e, can a magnetic field produce an electric current? Explain with the help of an appropriate example.
