Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the two names in the following diagram.
Fleming’s right hand rule.
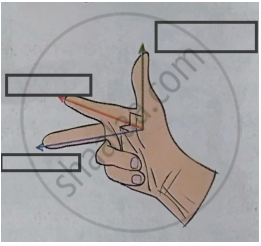
उत्तर

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
State the factors on which the strength of an electromagnet depends. How does it depend on these factors?
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
What do you understand by the term "electromagnetic induction"? Explain with the help of a diagram.
A light metal disc on the top of an electromagnet is thrown up as the current is switched on. Why? Give reason.
Show diagrammatically how an alternating emf is generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rotating loop.
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
Can a transformer work when it is connected to a D.C. source? Give a reason.
The diagram 10 shows two coils X and Y. The coil X is connected to a battery S and a key K. The coil Y is connected to a galvanometer G.
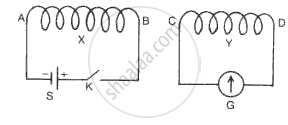
When the key K is closed. State the polarity
(i)At the end of the coil X,
(ii)At the end C of the coil Y,
(iii)At the end C of the coil Y if the coil Y is (a) Moved towards the coil X, (b) Moved away from the coil X.
Fig. shows a simple form of an A.C. generator.

(a) Name the parts labeled A and B.
(b) What would be the effect of doubling the number of turns on the coil if the speed of rotation remains unchanged?
(c) Which of the output terminals is positive if the coil is rotating in the
direction shown in the diagram (anticlockwise)?
( d ) What is the position of the rotating coil when p.d. across its ends is zero? Explain why p.d. is zero when the coil is at this position .
(e) Sketch a graph showing how the p.d. across the ends of the rotating coil varies with time for an A.C. dynamo.
( f) On th e same sheet of paper and vertically below the first graph using the same time scale, sketch graphs to show the effect of
(i) Doubling the speed of rotation and at the same time keeping
the field and the number of turns constant,
(ii ) Doubling the number of turns on the coil and at the same time
doubling the speed of rotation of the coil, keeping th e speed
constant.
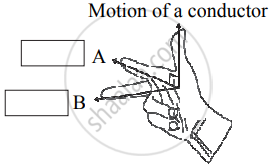
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
Answer the following:
State the principles of the electric motor and electric generator.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
List some of the practical applications of an electromagnet.
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
You have been provided with a solenoid AB.
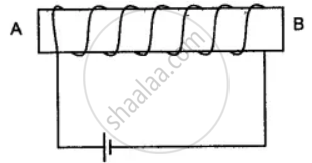
(i) What is the polarity at end A?
(ii) Give one advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
State the condition at which we say the two coils kept close to each other are perfectly coupled with each other.
Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
What for an inductor is used? Give some examples.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 4 A. If the magnetic flux through the coil is 6 x 10-5 Wb, find the magnetic energy stored in the medium surrounding the coil.
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
An alternating emf of 0.2 V is applied across an L-C-R series circuit having R = 4Q, C = 80µF, and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is
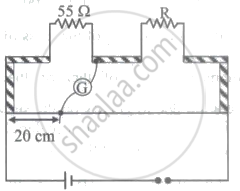
Shown in the figure below is a metre bridge set up with null deflection in the galvanometer. The value of the unknown resistance R is ______
A layer of atmosphere that reflects medium frequency radio waves which is ineffective during night, is ______.
A cylindrical bar magnet (A) and similar unmagnetized cylindrical iron bar (B) are dropped through metallic pipe. The time taken to come down by ____________.
There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then ______.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
What will be observed when the Magnet starts oscillating through the coil. Explain the reason behind this observation.
Induced current flows through a coil ______.
A coil of one turn is made of a wire of certain length and then from the same length, a coil of two turns is made. If the same current is passed in both the cases, then the ratio of the magnetic inductions at their centres will be:
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
One solenoid is centered inside another. The outer one has a length of 50.0 cm and contains 6750 coils, while the coaxial inner solenoid is 3.0 cm long and π cm2 in area and contains 150 coils. The current in the outer solenoid is changing at 3000 A/s. The emf induced in the inner solenoid is ______ V.
(Round off to two decimal places.)
Show that for a given positive ion species in a cyclotron, (i) the radius of their circular path inside a dee is directly proportional to their speed, and (ii) the maximum ion energy achievable is directly proportional to the square of the magnetic induction.
