Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
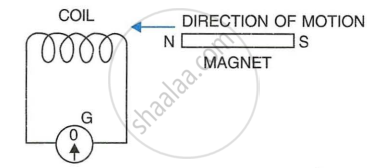
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
Solution
-
- When the magnet is moved rapidly in the direction of arrow, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes and there is a deflection in the galvanometer, indicating a flow of current through the coil.
- On keeping the magnet still, the magnetic flux linked with the coil does not change and there is no deflection in the galvanometer, indicating that no current is flowing through the coil.
- When the magnet is rapidly pulled out, there is again change in the magnetic flux linked with the coil and the galvanometer shows a deflection but this time in opposite direction, indicating that a current is flowing in opposite direction in the coil.
- If a more powerful magnet is used, deflection in the galvanometer will be large, indicating a greater amount of current.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
A circular coil of cross-sectional area 200 cm2 and 20 turns is rotated about the vertical diameter with angular speed of 50 rad s−1 in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 3.0 × 10−2T. Calculate the maximum value of the current in the coil.
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
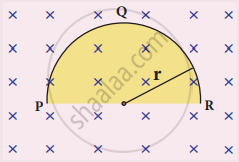
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
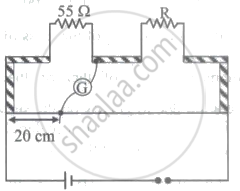
Shown in the figure below is a metre bridge set up with null deflection in the galvanometer. The value of the unknown resistance R is ______
What should be the core of an electromagnet?
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
For making a strong electromagnet the material of the core should be ______.
A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2×10 -3T. Find the force on the conductor.
