Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
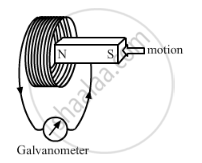
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
Solution
(1) The effect is called electromagnetic induction. It causes production of an induced current in the coil on the movement of the magnet.
(2) The reading shown on the galvanometer will be on the left side when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) Two changes noticed in the reading on the galvanometer:
- The deflection of galvanometer will be more to the right side.
- The deflection will occur more quickly.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
Name two devices in which electromagnets are used and two devices where permanent magnets are used.
Name and state the law which determines the direction of induced current.
or
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
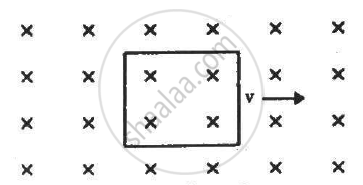
A conducting square loop of side l and resistance R moves in its plane with a uniform velocity v perpendicular to one of its sides. A uniform and constant magnetic field Bexists along the perpendicular to the plane of the loop as shown in figure. The current induced in the loop is _____________ .
The diagram 10 shows two coils X and Y. The coil X is connected to a battery S and a key K. The coil Y is connected to a galvanometer G.
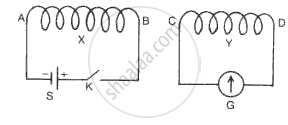
When the key K is closed. State the polarity
(i)At the end of the coil X,
(ii)At the end C of the coil Y,
(iii)At the end C of the coil Y if the coil Y is (a) Moved towards the coil X, (b) Moved away from the coil X.
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
The right-hand thumb rule is also called _______ rule.
A layer of atmosphere that reflects medium frequency radio waves which is ineffective during night, is ______.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
What will be observed when the Magnet starts oscillating through the coil. Explain the reason behind this observation.
