Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
A horizontal conducting rod 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed 5.0 ms–1 at right angles to the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field, 0.3 × 10–4 Wb m–2. Find the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rod.
उत्तर
Length of the wire, l = 10 m
Falling speed of the wire, v = 5.0 m/s
Magnetic field strength, B = 0.3 × 10–4 Wb m–2
- Emf induced in the wire,
e = Blv
= 0.3 × 10–4 × 5 × 10
= 1.5 × 10–3 V - Using Fleming’s right-hand rule, it can be inferred that the direction of the induced emf is from West to East.
- The eastern end of the wire is at a higher potential.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The magnetic flux through a loop varies according to the relation Φ = 8t2 + 6t + C, where ‘C’ is constant, 'Φ' is in milliweber and 't' is in second. What is the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in the loop at t = 2 seconds.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
The north-south polarities of an electromagnet can be found easily by using:
(a) Fleming's right-hand rule
(b) Fleming's left-hand rule
(c) Clock face rule
(d) Left-hand thumb rule
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be:
(a) north pole
(b) east pole
(c) south pole
(d) west pole
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
When Puja, a student of 10th class, watched her mother washing clothes in the open, she observed coloured soap bubbles and was curious to know why the soap bubbles appear coloured. In the evening when her father, an engineer by profession, came home, she asked him this question. Her father explained to her the basic phenomenon of physics due to which the soap bubbles appear coloured.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Puja and her father?
(b) State the phenomenon of light involved in the formation of coloured soap bubbles.
Show diagrammatically how an alternating emf is generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rotating loop.
Can a transformer work when it is connected to a D.C. source? Give a reason.
The diagram 10 shows two coils X and Y. The coil X is connected to a battery S and a key K. The coil Y is connected to a galvanometer G.
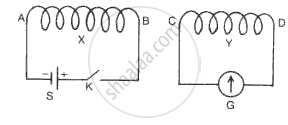
When the key K is closed. State the polarity
(i)At the end of the coil X,
(ii)At the end C of the coil Y,
(iii)At the end C of the coil Y if the coil Y is (a) Moved towards the coil X, (b) Moved away from the coil X.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
D.C. motor ______.
Why soft iron is preferred to be used as the core of the electromagnet of an electric bell?
Which of the following scientist invented the rule of electromagnetic induction?
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
The working of a dynamo is based on the principle of
A current I = 10 sin(100π t) A is passed in first coil, which induces a maximum e.m.f of 5π volt in second coil. The mutual inductance between the coils is ______.
