Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
A horizontal conducting rod 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed 5.0 ms–1 at right angles to the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field, 0.3 × 10–4 Wb m–2. Find the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rod.
उत्तर
Length of the wire, l = 10 m
Falling speed of the wire, v = 5.0 m/s
Magnetic field strength, B = 0.3 × 10–4 Wb m–2
- Emf induced in the wire,
e = Blv
= 0.3 × 10–4 × 5 × 10
= 1.5 × 10–3 V - Using Fleming’s right-hand rule, it can be inferred that the direction of the induced emf is from West to East.
- The eastern end of the wire is at a higher potential.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
What is electromagnetic induction?
Explain why, the core of an electromagnet should be of soft iron and not of steel.
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
The current is stopped in a wire held near a loop of wire .
A light metal disc on the top of an electromagnet is thrown up as the current is switched on. Why? Give reason.
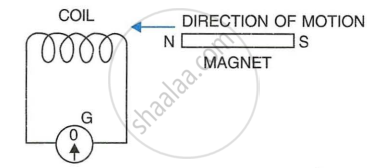
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
The right-hand thumb rule is also called _______ rule.
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
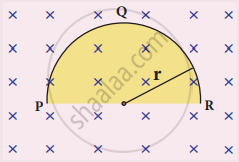
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
The instrument that use to defect electric current in the circuit is known as ____________.
Induced current flows through a coil ______.
Sea turtles return to their birth beach many decades after they were born due to ______.
Which of the following phenomena makes use of electromagnetic induction?
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
Show that for a given positive ion species in a cyclotron, (i) the radius of their circular path inside a dee is directly proportional to their speed, and (ii) the maximum ion energy achievable is directly proportional to the square of the magnetic induction.
Which type of force is experienced by a moving charge in a magnetic field?
