Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is electromagnetic induction?
उत्तर
The phenomenon of producing an induced e.m.f in a conductor or conducting coil due to changing magnetic flux is called electromagnetic induction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A solenoid of length 1.5 m and 4 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns per metre. A current of 5 A is flowing through it. The magnetic induction at a point inside the solenoid along the axis is ............................. .
(μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am)
- π × 10-5 T
- 2π × 10-5 T
- 3π × 10-5 T
- 4π × 10-5 T
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loud speaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area 2 cm2 with 25 closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the field region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick 90° turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in the coil (measured by a ballistic galvanometer connected to coil) is 7.5 mC. The combined resistance of the coil and the galvanometer is 0.50 Ω. Estimate the field strength of magnet.
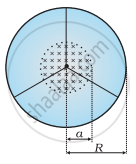
A line charge λ per unit length is lodged uniformly onto the rim of a wheel of mass M and radius R. The wheel has light non-conducting spokes and is free to rotate without friction about its axis (Figure). A uniform magnetic field extends over a circular region within the rim. It is given by,
B = − B0 k (r ≤ a; a < R)
= 0 (otherwise)
What is the angular velocity of the wheel after the field is suddenly switched off?
Prove theoretically (electromagnetic induction) `e = (dphi)/(dt)`
If ‘R’ is the radius of dees and ‘B’ be the magnetic field of induction in which positive charges (q) of mass (m) escape from the cyclotron, then its maximum speed (vmax) is _______.
A) `(qR)/(Bm)`
B)`(qm)/(Br)`
C) `(qBR)/m`
D) `m/(qBR)`
A circular coil of cross-sectional area 200 cm2 and 20 turns is rotated about the vertical diameter with angular speed of 50 rad s−1 in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 3.0 × 10−2T. Calculate the maximum value of the current in the coil.
Name a common device that uses electromagnets.
State three ways in which the strength of an electromagnet can be increased.
What is an electromagnet? Describe the construction and working of an electromagnet with the help of a labelled diagram.
Explain why, an electromagnet is called a temporary magnet.
State the factors on which the strength of an electromagnet depends. How does it depend on these factors?
The north-south polarities of an electromagnet can be found easily by using:
(a) Fleming's right-hand rule
(b) Fleming's left-hand rule
(c) Clock face rule
(d) Left-hand thumb rule
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A motor works on the principle electric generator?
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
What do you understand by the term "electromagnetic induction"? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Name one device which works on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
An induced current is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil. The magnitude of induced current does not depend on:
(a) the speed with which the magnet is moved
(b) the number of turns of the coil
(c) the resistivity of the wire of the coil
(d) the strength of the magnet
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
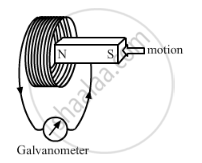
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A loop of wire is held near a magnet.
Welders wear special glass goggles while working. Why? Explain.
When Puja, a student of 10th class, watched her mother washing clothes in the open, she observed coloured soap bubbles and was curious to know why the soap bubbles appear coloured. In the evening when her father, an engineer by profession, came home, she asked him this question. Her father explained to her the basic phenomenon of physics due to which the soap bubbles appear coloured.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Puja and her father?
(b) State the phenomenon of light involved in the formation of coloured soap bubbles.
Consider the energy density in a solenoid at its centre and that near its ends. Which of the two is greater?
A conducting rod is moved with a constant velocity v in a magnetic field. A potential difference appears across the two ends _____________ .
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation l. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
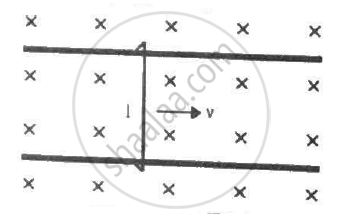
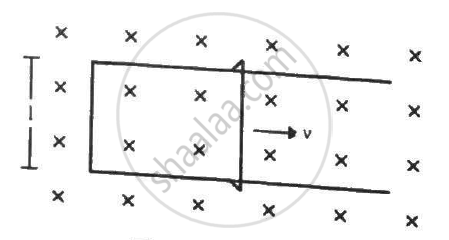
Figure shows a long U-shaped wire of width l placed in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A wire of length l is slid on the U-shaped wire with a constant velocity v towards right. The resistance of all the wires is r per unit length. At t = 0, the sliding wire is close to the left edge of the U-shaped wire. (a) Calculate the force needed to keep the sliding wire moving with a constant velocity v. (b) If the force needed just after t = 0 is F0, find the time at which the force needed will be F0/2.0
Can a transformer work when it is connected to a D.C. source? Give a reason.
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-down transformer.
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-up transformer.
Fig. shows a simple form of an A.C. generator.

(a) Name the parts labeled A and B.
(b) What would be the effect of doubling the number of turns on the coil if the speed of rotation remains unchanged?
(c) Which of the output terminals is positive if the coil is rotating in the
direction shown in the diagram (anticlockwise)?
( d ) What is the position of the rotating coil when p.d. across its ends is zero? Explain why p.d. is zero when the coil is at this position .
(e) Sketch a graph showing how the p.d. across the ends of the rotating coil varies with time for an A.C. dynamo.
( f) On th e same sheet of paper and vertically below the first graph using the same time scale, sketch graphs to show the effect of
(i) Doubling the speed of rotation and at the same time keeping
the field and the number of turns constant,
(ii ) Doubling the number of turns on the coil and at the same time
doubling the speed of rotation of the coil, keeping th e speed
constant.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
Answer the following:
State the principles of the electric motor and electric generator.
What is an electromagnet? List any two uses.
Draw a labelled diagram to show how an electromagnet is made.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
List some of the practical applications of an electromagnet.
You have been provided with a solenoid AB.
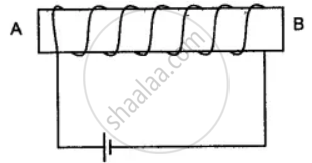
(i) What is the polarity at end A?
(ii) Give one advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
Choose the correct option:
A conductor rod of length (l) is moving with velocity (v) in a direction normal to a uniform magnetic field (B). What will be the magnitude of induced emf produced between the ends of the moving conductor?
Fleming's left hand rule : electric current : : Fleming's right hand rule : _______
Write Fleming’s right hand thumb rule with the help of diagram.
State Lenz’s law.
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
Give an illustration of determining direction of induced current by using Lenz’s law.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 0.4 A. If the magnetic flux of 4 mWb is linked with each turn of the coil, find the inductance of the coil.
An alternating emf of 0.2 V is applied across an L-C-R series circuit having R = 4Q, C = 80µF, and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is
We can induce the current in a coil by ____________.
What should be the core of an electromagnet?
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
What will be observed when the Magnet starts oscillating through the coil. Explain the reason behind this observation.
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
Which of the following instruments works by electromagnetic induction?
For making a strong electromagnet the material of the core should be ______.
A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2×10 -3T. Find the force on the conductor.
The working of a dynamo is based on the principle of
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
A conducting bar of length L is free to slide on two parallel conducting rails as shown in the figure
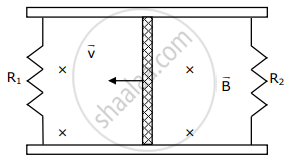
Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected across the ends of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` pointing into the page. An external agent pulls the bar to the left at a constant speed v. The correct statement about the directions of induced currents I1 and I2 flowing through R1 and R2 respectively is:
Show that for a given positive ion species in a cyclotron, (i) the radius of their circular path inside a dee is directly proportional to their speed, and (ii) the maximum ion energy achievable is directly proportional to the square of the magnetic induction.
