Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
उत्तर
The device used for producing electric current is called a generator.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
When a bar magnet is pushed towards (or away) from the coil connected to a galvanometer, the pointer in the galvanometer deflects. Identify the phenomenon causing this deflection and write the factors on which the amount and direction of the deflection depends. State the laws describing this phenomenon.
Prove theoretically (electromagnetic induction) `e = (dphi)/(dt)`
When an electric current is passed through any wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. Then why an electric iron connecting cable does not attract nearby iron objects when electric current switched on through it?
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
What condition is necessary for the production of current by electromagnetic induction?
Name one device which works on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A magnet is moved through a loop of wire .
Show diagrammatically how an alternating emf is generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rotating loop.
Draw and label the diagram of a simple D.C. motor.
(a) Explain the rotation of the coil, giving a reason for your answer.
(b) How can you reverse the direction of rotation of the armature?
(c) How can you increase the speed of rotation of the motor?
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
A. C. generator______.
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
List some of the practical applications of an electromagnet.
Why soft iron is preferred to be used as the core of the electromagnet of an electric bell?
Draw a labelled diagram to make an electromagnet from a soft iron bar. Mark the polarity at its ends in your diagram. What precaution would you observe while making it?
You have been provided with a solenoid AB.
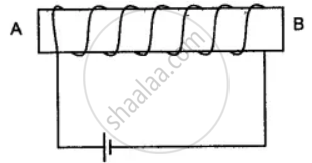
(i) What is the polarity at end A?
(ii) Give one advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
The energy stored in a 50 mH inductor carrying a current of 4 A is ______
State the condition at which we say the two coils kept close to each other are perfectly coupled with each other.
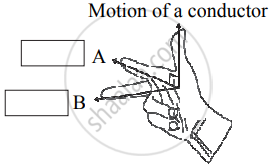
Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
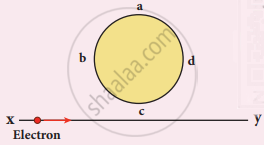
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
Show that Lenz’s law is in accordance with the law of conservation of energy.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
A straight metal wire crosses a magnetic field of flux 4 mWb in a time 0.4 s. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the wire.
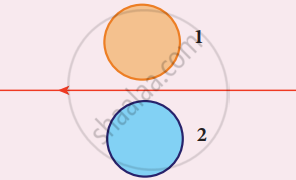
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then ______.
The condition for the praenomen of electromagnetic induction is that there must be a relative motion between ____________.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2×10 -3T. Find the force on the conductor.
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
An expression for oscillating electric field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given as Ez = 300 sin(5π × 103x - 3π × 1011t)Vm-1 Then, the value of magnetic field amplitude will be ______. (Given: speed of light in Vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
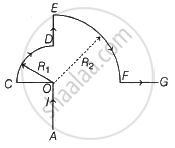
In the current carrying conductor (AOCDEFG) as shown, the magnetic induction at point O is ______.
(R1 and R2 are radii of CD and EF respectively. l = current in the loop, μ0 = permeability of free space)