Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
उत्तर
The device used for producing electric current is called a generator.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
The magnetic flux through a loop is varying according to a relation `phi = 6t^2 + 7t + 1` where `phi` is in milliweber and t is in second. What is the e.m.f. induced in the loop at t = 2 second?
A circular coil of cross-sectional area 200 cm2 and 20 turns is rotated about the vertical diameter with angular speed of 50 rad s−1 in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 3.0 × 10−2T. Calculate the maximum value of the current in the coil.
State three ways in which the strength of an electromagnet can be increased.
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
Explain why, an electromagnet is called a temporary magnet.
The most suitable material for making the core of an electromagnet is:
(a) soft iron
(b) brass
(c) aluminium
(d) steel
What condition is necessary for the production of current by electromagnetic induction?
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A motor works on the principle electric generator?
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
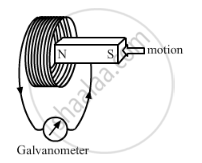
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A magnet is moved through a loop of wire .
A conducting square loop having edges of length 2.0 cm is rotated through 180° about a diagonal in 0.20 s. A magnetic field B exists in the region which is perpendicular to the loop in its initial position. If the average induced emf during the rotation is 20 mV, find the magnitude of the magnetic field.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
A. C. generator______.
A transformer has 400 turns in the primary winding and 10 turns in the secondary winding. The primary e.m.f. is 250 V and the primary current is 2.0 A. calculate:
(a) The secondary voltage,
(b) The secondary current, assuming 100% efficiency.
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
Give an illustration of determining direction of induced current by using Lenz’s law.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
The magnetic flux passing through a coil perpendicular to its plane is a function of time and is given by OB = (2t3 + 4t2 + 8t + 8) Wb. If the resistance of the coil is 5 Ω, determine the induced current through the coil at a time t = 3 second.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
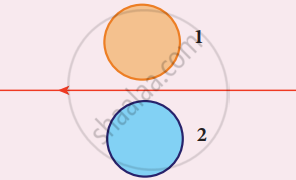
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
An alternating emf of 0.2 V is applied across an L-C-R series circuit having R = 4Q, C = 80µF, and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is
A cylindrical bar magnet is kept along the axis of a circular coil. If the magnet is rotated about its axis, then ____________.
What should be the core of an electromagnet?
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
What will be observed when the Magnet starts oscillating through the coil. Explain the reason behind this observation.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
Name some equipment that uses electromagnetism for functioning.
Which of the following phenomena makes use of electromagnetic induction?
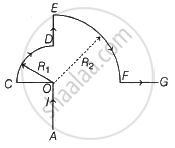
In the current carrying conductor (AOCDEFG) as shown, the magnetic induction at point O is ______.
(R1 and R2 are radii of CD and EF respectively. l = current in the loop, μ0 = permeability of free space)
The charge will flow through a galvanometer of resistance 200Ω connected to a 400Ω circular coil of 1000 turns wound on a wooden stick 20 mm in diameter, if a magnetic field B = 0.012 T parallel to the axis of the stick decreased suddenly to zero, is near ______.
