Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Current Electricity
3: Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current
▶ 4: Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current
5: Electromagnetic waves
6: Ray Optics
7: Wave Optics
8: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
9: Atomic and Nuclear physics
10: Electronics and Communication
11: Recent Developments in Physics
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 4 - Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 4 - Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board 4 Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current Evaluation [Pages 257 - 264]
Multiple Choice Questions
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
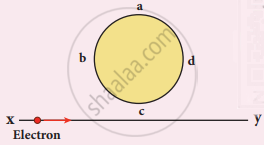
The current will reverse its direction as the electron goes past the coil
No current will be induced
abcd
adcb
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
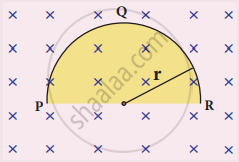
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
Zero
`("Bv"pi"r"^2)/2` and P is at higher potential
πrBv and R is at higher potential
2rBv and R is at higher potential
The flux linked with a coil at any instant t is given by ΦB = − 10t2 - 50t + 250. The induced emf at t = 3 s is
- 190 V
- 10 V
10 V
190 V
When the current changes from +2A to −2A in 0.05 s, an emf of 8 V is induced in a coil. The co-efficient of self-induction of the coil is
0.2 H
0.4 H
0.8 H
0.1 H
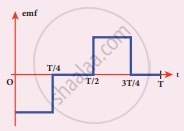
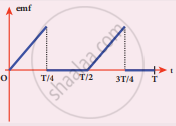
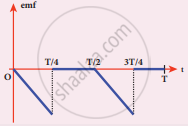
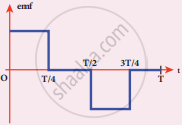
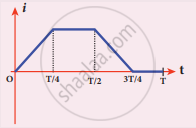
The current i flowing in a coil varies with time as shown in the figure. The variation of induced emf with time would be
A circular coil with a cross-sectional area of 4 cm2 has 10 turns. It is placed at the centre of a long solenoid that has 15 turns/cm and a cross-sectional area of 10 cm2. The axis of the coil coincides with the axis of the solenoid. What is their mutual inductance?
7.54 µH
8.54 µH
9.54 µH
10.54 µH
In a transformer, the number of turns in the primary and the secondary are 410 and 1230 respectively. If the current in primary is 6A, then that in the secondary coil is
2 A
18 A
12 A
1 A
A step-down transformer reduces the supply voltage from 220 V to 11 V and increase the current from 6 A to 100 A. Then its efficiency is
1.2
0.83
0.12
0.9
In an electrical circuit, R, L, C, and AC voltage sources are all connected in series. When L is removed from the circuit, the phase difference between the voltage and current in the circuit is `π/3`. Instead, if C is removed from the circuit, the phase difference is again `π/3`. The power factor of the circuit is
`1/2`
`1/sqrt2`
1
`sqrt3/2`
In a series RL circuit, the resistance and inductive reactance are the same. Then the phase difference between the voltage and current in the circuit is
`pi/4`
`pi/2`
`pi/6`
zero
In a series resonant RLC circuit, the voltage across 100 Ω resistor is 40 V. The resonant frequency ω is 250 rad/s. If the value of C is 4 µF, then the voltage across L is
600 V
4000 V
400 V
1 V
An inductor 20 mH, a capacitor 50 μF and a resistor 40Ω are connected in series across a source of emf V = 10 sin 340 t. The power loss in AC circuit is
0.76 W
0.89 W
0.46 W
0.67 W
The instantaneous values of alternating current and voltage in a circuit are
i = `1/sqrt2` sin 100π A and
v = `1/sqrt2 sin (100 pi"t" + pi/3)"V"`.
The average power in watts consumed in the circuit is
`1/4`
`sqrt3/4`
`1/2`
`1/8`
In an oscillating LC circuit, the maximum charge on the capacitor is Q. The charge on the capacitor when the energy is stored equally between the electric and magnetic fields is
`"Q"/2`
`"Q"/sqrt3`
`"Q"/sqrt2`
Q
`20/pi^2`H inductor is connected to a capacitor of capacitance C. The value of C in order to impart maximum power at 50 Hz is
50 μF
0.5 μF
500 μF
5 μF
What is electromagnetic induction?
State Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction.
State Lenz’s law.
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
How is Eddy current produced? How do they flow in a conductor?
Mention the ways of producing induced emf.
What for an inductor is used? Give some examples.
What do you mean by self-induction?
What is meant by mutual induction?
Give the principle of AC generator.
List out the advantages of stationary armature-rotating field system of AC generator.
What are step-up and step-down transformers?
Define average value of an alternating current.
How will you define RMS value of an alternating current?
What are phasors?
Define electric resonance.
What do you mean by resonant frequency?
How will you define Q-factor?
What is meant by wattles current?
Give any one definition of power factor.
What are LC oscillations?
Long Answer Questions
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
Give an illustration of determining direction of induced current by using Lenz’s law.
Show that Lenz’s law is in accordance with the law of conservation of energy.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
Give the uses of Foucault current.
Define self-inductance of a coil interms of
- magnetic flux and
- induced emf
How will you define the unit of inductance?
What do you understand by self-inductance of a coil?
Give the physical significance of self-inductance of a coil.
Assuming that the length of the solenoid is large when compared to its diameter, find the equation for its inductance.
An inductor of inductance L carries an electric current i. How much energy is stored while establishing the current in it?
Show that the mutual inductance between a pair of coils is same (M12 = M21).
How will you induce an emf by changing the area enclosed by the coil?
Show mathematically that the rotation of a coil in a magnetic field over one rotation induces an alternating emf of one cycle.
Elaborate the standard construction details of AC generator.
Explain the working of a single-phase AC generator with necessary diagram.
How are the three different emfs generated in a three-phase AC generator? Show the graphical representation of these three emfs.
Explain the construction of transformer.
Explain the working of the transformer.
Mention the various energy losses in a transformer.
Give the advantage of AC in long distance power transmission with an illustration.
Find out the phase relationship between voltage and current in a pure inductive circuit.
Derive an expression for phase angle between the applied voltage and current in a series RLC circuit.
Define inductive reactance and give its units.
Define capacitive reactance. Give its units.
Obtain an expression for average power of AC over a cycle. Discuss its special cases.
Explain the generation of LC oscillations in a circuit containing an inductor of inductance L and a capacitor of capacitance C.
Show that the total energy is conserved during LC oscillations.
Prove that energy is conserved during electromagnetic induction.
Numerical problems
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
A straight metal wire crosses a magnetic field of flux 4 mWb in a time 0.4 s. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the wire.
The magnetic flux passing through a coil perpendicular to its plane is a function of time and is given by OB = (2t3 + 4t2 + 8t + 8) Wb. If the resistance of the coil is 5 Ω, determine the induced current through the coil at a time t = 3 second.
A closely wound circular coil of radius 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field. When the magnetic field is changed from 8000 T to 2000 T in 6 s, an emf of 44 V is induced in it. Calculate the number of turns in the coil.
A rectangular coil of area 6 cm2 having 3500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. Initially, the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field and is then rotated through an angle of 180°. If the resistance of the coil is 35 Ω, find the amount of charge flowing through the coil.
An induced current of 2.5 mA flows through a single conductor of resistance 100 Ω. Find out the rate at which the magnetic flux is cut by the conductor.
A fan of metal blades of length 0.4 m rotates normal to a magnetic field of 4 x 10-3 T. If the induced emf between the centre and edge of the blade is 0.02 V, determine the rate of rotation of the blade.
A bicycle wheel with metal spokes of 1 m long rotates in Earth’s magnetic field. The plane of the wheel is perpendicular to the horizontal component of Earth’s field of 4 x 10-5 T. If the emf induced across the spokes is 31.4 mV, calculate the rate of revolution of the wheel.
Determine the self-inductance of 4000 turn air-core solenoid of length 2m and diameter 0.04 m.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 4 A. If the magnetic flux through the coil is 6 x 10-5 Wb, find the magnetic energy stored in the medium surrounding the coil.
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 0.4 A. If the magnetic flux of 4 mWb is linked with each turn of the coil, find the inductance of the coil.
Two air core solenoids have the same length of 80 cm and same cross–sectional area 5 cm2. Find the mutual inductance between them if the number of turns in the first coil is 1200 turns and that in the second coil is 400 turns.
A long solenoid having 400 turns per cm carries a current 2A. A 100 turn coil of cross-sectional area 4 cm2 is placed co-axially inside the solenoid so that the coil is in the field produced by the solenoid. Find the emf induced in the coil if the current through the solenoid reverses its direction in 0.04 sec.
A 200 turn circular coil of radius 2 cm is placed co-axially within a long solenoid of 3 cm radius. If the turn density of the solenoid is 90 turns per cm, then calculate mutual inductance of the coil and the solenoid.
The solenoids S1 and S2 are wound on an iron-core of relative permeability 900. The area of their cross-section and their length are the same and are 4 cm2 and 0.04 m, respectively. If the number of turns in S1 is 200 and that in S2 is 800, calculate the mutual inductance between the coils. The current in solenoid 1 is increased from 2A to 8A in 0.04 second. Calculate the induced emf in solenoid 2.
A step-down transformer connected to the main supply of 220 V is used to operate 11V,88W lamp. Calculate
- Voltage transformation ratio and
- Current in the primary
A 200V/120V step-down transformer of 90% efficiency is connected to an induction stove of resistance 40 Ω. Find the current drawn by the primary of the transformer.
The 300 turn primary of a transformer has resistance 0.82 Ω and the resistance of its secondary of 1200 turns is 6.2 Ω. Find the voltage across the primary if the power output from the secondary at 1600V is 32 kW. Calculate the power losses in both coils when the transformer efficiency is 80%
Calculate the instantaneous value at 60°, average value and RMS value of an alternating current whose peak value is 20 A.
Conceptual Questions
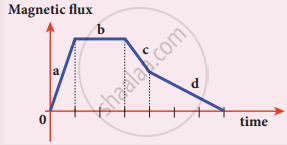
A graph between the magnitude of the magnetic flux linked with a closed-loop and time is given in the figure. Arrange the regions of the graph in ascending order of the magnitude of induced emf in the loop.
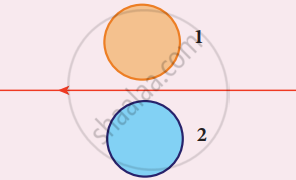
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
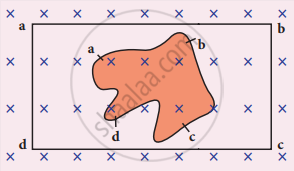
A flexible metallic loop abcd in the shape of a square is kept in a magnetic field with its plane perpendicular to the field. The magnetic field is directed into the paper normally. Find the direction of the induced current when the square loop is crushed into an irregular shape as shown in the figure.
Predict the polarity of the capacitor in a closed circular loop when two bar magnets are moved as shown in the figure.

In a series LC circuit, the voltages across L and C are 180° out of phase. Is it correct? Explain.
When does power factor of a series RLC circuit become maximum?
Solutions for 4: Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 4 - Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 4 - Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 4 - Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 4 (Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 4 Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current are Electromagnetic Induction, Self–Induction, Transformers, Alternating Currents, Eddy Currents, Oscillation in LC Circuits, Methods of Producing Induced Emf, A.C. Generator, Power in AC Circuit.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board solutions Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.