Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find out the phase relationship between voltage and current in a pure inductive circuit.
उत्तर
Consider a circuit containing a pure inductor of inductance L connected across an alternating voltage source. The alternating voltage is given by the equation.
υ = Vm sin ωt …(1)
The alternating current flowing through the inductor induces a self-induced emf or back emf in the circuit. The back emf is given by
Back emf, ε -L `"di"/"dt"`
By applying Kirchoff’s loop rule to the purely inductive circuit, we get
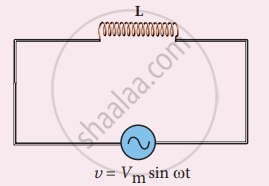
AC circuit with inductor
υ + ε = 0
Vm sin ωt = L`"di"/"dt"`
di = L`"V"_"m"/"L"` sin ωt dt
i = `"V"_"m"/"L" int` sin ωt dt = `"V"_"m"/"L"_omega` (-cos ωt) + constant
The integration constant in the above equation is independent of time. Since the voltage in the circuit has only time dependent part, we can set the time independent part in the current (integration constant) into zero.
`[(cos omega"t" = sin(pi/2 - omega"t")),(- sin (pi/2 - omega"t") = sin (omega"t" - pi/2))]`
i = `"V"_"m"/"L"_omega sin (omega"t" - pi/2) or ` i = `"I"_"m" sin(omega"t" - pi/2)` ....(2)
where `"V"_"m"/"L"_omega = "I"_"m"`, the peak value of the alternating current in the circuit. From equation (1) and (2), it is evident that current lags behind the applied voltage by `pi/2` in an inductive circuit.
This fact is depicted in the phasor diagram. In the wave diagram also, it is seen that current lags the voltage by 90°.
Inductive reactance XL:
The peak value of current Im is given by Im = `"V"_"m"/"L"_omega`. Let us compare this equation with Im = `"V"_"m"/"R"` from resistive circuit. The equantity ωL Plays the same role as the resistance in resistive circuit. This is the resistance offered by the inductor, called inductive reactance (XL). It is measured in ohm.
XL = ωL
The inductive reactance (XL) varies directly as the frequency.
XL = 2πfL …….. (3)
where ƒ is the frequency of the alternating current. For a steady current, ƒ= 0. Therefore, XL = 0. Thus an ideal inductor offers no resistance to steady DC current.

Phasor diagram and wave diagram for AC circuit with L
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name two factors on which the magnitude of an induced e.m.f. in the secondary coil depends.
The teachers of Geeta’s school took the students on a study trip to a power generating station, located nearly 200 km away from the city. The teacher explained that electrical energy is transmitted over such a long distance to their city, in the form of alternating current (ac) raised to a high voltage. At the receiving end in the city, the voltage is reduced to operate the devices. As a result, the power loss is reduced. Geeta listened to the teacher and asked questions about how the ac is converted to a higher or lower voltage.
1) Name the device used to change the alternating voltage to a higher or lower value. State one cause for power dissipation in this device.
2) Explain with an example, how power loss is reduced if the energy is transmitted over long distances as an alternating current rather than a direct current.
3) Write two values each shown by the teachers and Geeta.
The following diagram in Fig. 10.44 shows a coil X connected to a sensitive centre –zero galvanometer G and a coil P connected to a battery through a switch S.
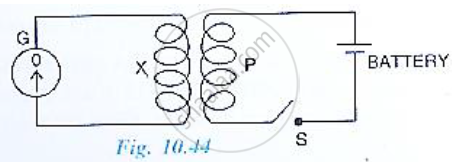
(a) Describe the observation when the switch S is (i) closed suddenly, (ii) then kept closed, (iii) finally opened.
(b) Name and state the law which explains the above observations.
For what purpose are the transformers used? Can they be used with a direct current source?
Mention the two characteristic properties of the material suitable for making core of a transformer.
Draw a labeled diagram of a full wave rectifier circuit. State its working principle. Show the input-output waveforms ?
An ideal transformer has 100 turns in the primary and 250 turns in the secondary. The peak value of the AC is 28 V. The rms secondary voltage is nearest to ______
A transformer operating at primary voltage 8 kV and secondary voltage 160 V serves a load of 80 kW. Assuming the transformer to be ideal with purely resistive load and working on unity power factor, the loads in the primary and secondary circuit would be:
Two coils P and Q are kept near each other. When no current flows through coil P and current increase in coil Q at the rate 10A/s, the emf in coil P is 15mV. When coil Q carries no current and current of 1. 8A flows through coil P, the magnetic flux linked with the coil Q is ______.
