Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find out the phase relationship between voltage and current in a pure inductive circuit.
उत्तर
Consider a circuit containing a pure inductor of inductance L connected across an alternating voltage source. The alternating voltage is given by the equation.
υ = Vm sin ωt …(1)
The alternating current flowing through the inductor induces a self-induced emf or back emf in the circuit. The back emf is given by
Back emf, ε -L `"di"/"dt"`
By applying Kirchoff’s loop rule to the purely inductive circuit, we get
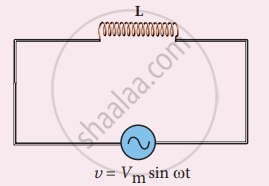
AC circuit with inductor
υ + ε = 0
Vm sin ωt = L`"di"/"dt"`
di = L`"V"_"m"/"L"` sin ωt dt
i = `"V"_"m"/"L" int` sin ωt dt = `"V"_"m"/"L"_omega` (-cos ωt) + constant
The integration constant in the above equation is independent of time. Since the voltage in the circuit has only time dependent part, we can set the time independent part in the current (integration constant) into zero.
`[(cos omega"t" = sin(pi/2 - omega"t")),(- sin (pi/2 - omega"t") = sin (omega"t" - pi/2))]`
i = `"V"_"m"/"L"_omega sin (omega"t" - pi/2) or ` i = `"I"_"m" sin(omega"t" - pi/2)` ....(2)
where `"V"_"m"/"L"_omega = "I"_"m"`, the peak value of the alternating current in the circuit. From equation (1) and (2), it is evident that current lags behind the applied voltage by `pi/2` in an inductive circuit.
This fact is depicted in the phasor diagram. In the wave diagram also, it is seen that current lags the voltage by 90°.
Inductive reactance XL:
The peak value of current Im is given by Im = `"V"_"m"/"L"_omega`. Let us compare this equation with Im = `"V"_"m"/"R"` from resistive circuit. The equantity ωL Plays the same role as the resistance in resistive circuit. This is the resistance offered by the inductor, called inductive reactance (XL). It is measured in ohm.
XL = ωL
The inductive reactance (XL) varies directly as the frequency.
XL = 2πfL …….. (3)
where ƒ is the frequency of the alternating current. For a steady current, ƒ= 0. Therefore, XL = 0. Thus an ideal inductor offers no resistance to steady DC current.

Phasor diagram and wave diagram for AC circuit with L
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the function of a transformer.
Name the transformer used in the power transmitting station of a power plant.
Name the phenomenon ?
Explain why an induced current must flow in such a direction so as to oppose the change producing it.
Why is the iron core of a transformer made laminated (thin sheets) instead of being in one solid piece?
A transformer is designed to work from a 240 V a.c. mains and to give a supply of 8 V to ring a house bell. The primary coil has 4800 turns. How many turns will be in the secondary coil?
A transformer is essentially an a.c. device. It cannot work on d.c. It changes alternating voltages or currents. It does not affect the frequency of a.c. It is based on the phenomenon of mutual induction. A transformer essentially consists of two coils of insulated copper wire having different numbers of turns and wound on the same soft iron core.
The number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of an ideal transformer is 2000 and 50 respectively. The primary coil is connected to a main supply of 120 V and secondary coil is connected to a bulb of resistance 0.6 Ω.
The value of current in primary coil is ______.
A transformer operating at primary voltage 8 kV and secondary voltage 160 V serves a load of 80 kW. Assuming the transformer to be ideal with purely resistive load and working on unity power factor, the loads in the primary and secondary circuit would be:
Two coils P and Q are kept near each other. When no current flows through coil P and current increase in coil Q at the rate 10A/s, the emf in coil P is 15mV. When coil Q carries no current and current of 1. 8A flows through coil P, the magnetic flux linked with the coil Q is ______.
