Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Elaborate the standard construction details of AC generator.
उत्तर
Construction:
Alternator consists of two major parts, namely stator and rotor. As their names suggest, stator is stationary while rotor rotates inside the stator. In any standard construction of commercial alternators, the armature winding is mounted on stator and the field magnet on rotor. The construction details of stator, rotor and various other components involved in them are given below.
- Stator:
The stationary part which has armature windings mounted in it is called stator. It has three components, namely stator frame, stator core and armature winding.
- Stator core:
Stator core or armature core is made up of iron or steel alloy. It is a hollow cylinder and is laminated to minimize eddy current loss. The slots are cut on inner surface of the core to accommodate armature windings. -
Armature winding:
Armature winding is the coil, wound on slots provided in the armature core. One or more than one coil may be employed, depending on the type of alternator. Two types of windings are commonly used. They are (i) single-layer winding and (ii) double-layer winding. In single-layer winding, a slot is occupied by a coil as a single layer. But in double-layer winding, the coils are split into two layers such as top and bottom layers.
- Rotor:
Rotor contains magnetic field windings. The magnetic poles are magnetized by DC source. The ends of field windings are connected to a pair of slip rings, attached to a common shaft about which the rotor rotates. Slip rings rotate along with rotor. To maintain a connection between the DC source and field windings, two brushes are used which. continuously slide over the slip rings.
There are 2 types of rotors used in alternators:
- Salient pole rotor:
The word salient means projecting. This rotor has a number of projecting poles having their bases riveted to the rotor. It is mainly used in low-speed alternators. - Cylindrical pole rotor:
This rotor consists of a smooth solid cylinder. The slots are cut on the outer surface of the cylinder along its length. It is suitable for very high-speed alternators.
The frequency of alternating emf induced is directly proportional to the rotor speed. In order to maintain the frequency constant, the rotor must run at a constant speed. These are standard construction details of alternators.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Describe briefly, with the help of a labelled diagram, the basic elements of an A.C. generator.
State A.C. generator underlying principle?
In an electrical circuit, R, L, C, and AC voltage sources are all connected in series. When L is removed from the circuit, the phase difference between the voltage and current in the circuit is `π/3`. Instead, if C is removed from the circuit, the phase difference is again `π/3`. The power factor of the circuit is
The instantaneous values of alternating current and voltage in a circuit are
i = `1/sqrt2` sin 100π A and
v = `1/sqrt2 sin (100 pi"t" + pi/3)"V"`.
The average power in watts consumed in the circuit is
List out the advantages of stationary armature-rotating field system of AC generator.
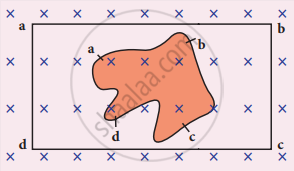
A flexible metallic loop abcd in the shape of a square is kept in a magnetic field with its plane perpendicular to the field. The magnetic field is directed into the paper normally. Find the direction of the induced current when the square loop is crushed into an irregular shape as shown in the figure.
When the plane of the armature of a generator is parallel to the field. in which it is rotating ______.
The average value of alternating current over a full cycle is always ______. [I0 = Peak value of current]
The coil of an ac generator consists of 100 turns of wire, each of area 0.5 m2. The resistance of the wire is 100 Ω. The coil is rotating in a magnetic field of 0.8 T perpendicular to its axis of rotation, at a constant angular speed of 60 radians per second. Calculate the maximum emf generated and power dissipated in the coil.
State the basic principle behind the working of an ac generator.
