Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Fleming's left hand rule : electric current : : Fleming's right hand rule : _______
उत्तर
Fleming's left hand rule : electric current : : Fleming's right hand rule : direction of induced current
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A solenoid of length 1.5 m and 4 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns per metre. A current of 5 A is flowing through it. The magnetic induction at a point inside the solenoid along the axis is ............................. .
(μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am)
- π × 10-5 T
- 2π × 10-5 T
- 3π × 10-5 T
- 4π × 10-5 T
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
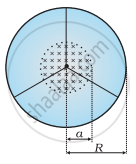
A line charge λ per unit length is lodged uniformly onto the rim of a wheel of mass M and radius R. The wheel has light non-conducting spokes and is free to rotate without friction about its axis (Figure). A uniform magnetic field extends over a circular region within the rim. It is given by,
B = − B0 k (r ≤ a; a < R)
= 0 (otherwise)
What is the angular velocity of the wheel after the field is suddenly switched off?
The magnetic flux through a loop is varying according to a relation `phi = 6t^2 + 7t + 1` where `phi` is in milliweber and t is in second. What is the e.m.f. induced in the loop at t = 2 second?
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
State the factors on which the strength of an electromagnet depends. How does it depend on these factors?
Write some of the important uses of electromagnets.
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A motor works on the principle electric generator?
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
When current is 'switched on' and 'switched off' in a coil, a current is induced in another coil kept near it. What is this phenomenon known as?
Describe different ways to induce current in a coil of wire.
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
Name and state the law which determines the direction of induced current.
or
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
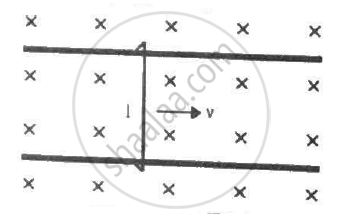
Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation l. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-down transformer.
The diagram 10 shows two coils X and Y. The coil X is connected to a battery S and a key K. The coil Y is connected to a galvanometer G.
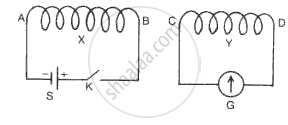
When the key K is closed. State the polarity
(i)At the end of the coil X,
(ii)At the end C of the coil Y,
(iii)At the end C of the coil Y if the coil Y is (a) Moved towards the coil X, (b) Moved away from the coil X.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
List some of the practical applications of an electromagnet.
What is an electromagnet? What do you know about the simplest form of an electromagnet?
Using Ampere's law, obtain an expression for the magnetic induction near a current-carrying straight infinitely long wire.
The right-hand thumb rule is also called _______ rule.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Write Fleming’s right hand thumb rule with the help of diagram.
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
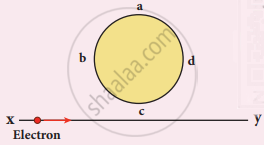
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
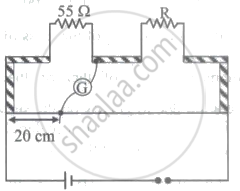
Shown in the figure below is a metre bridge set up with null deflection in the galvanometer. The value of the unknown resistance R is ______
A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2×10 -3T. Find the force on the conductor.
The working of a dynamo is based on the principle of
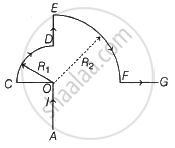
In the current carrying conductor (AOCDEFG) as shown, the magnetic induction at point O is ______.
(R1 and R2 are radii of CD and EF respectively. l = current in the loop, μ0 = permeability of free space)