Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2016-2017
Date & Time: 14th March 2017, 12:30 pm
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, if the incident violet light is replaced by red light? Give reason.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Name the phenomenon which shows the quantum nature of electromagnetic radiation.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
What is the direction of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 when current I in the wire is increasing steadily?
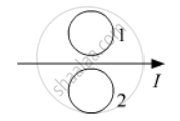
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
In which directions do the electric and magnetic field vectors oscillate in an electromagnetic wave propagating along the x-axis?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Nichrome and copper wires of same length and same radius are connected in series. Current I is passed through them. Which wire gets heated up more? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Write two properties of a material suitable for making a permanent magnet
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Write two properties of a material suitable for making an electromagnet.
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Draw the intensity pattern for single slit diffraction.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Draw the intensity pattern for double slit interference.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
State differences between interference and diffraction patterns.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Unpolarised light is passed through a polaroid P1. When this polarised beam passes through another polaroid P2 and if the pass axis of P2 makes angle θ with the pass axis of P1, then write the expression for the polarised beam passing through P2. Draw a plot showing the variation of intensity when θ varies from 0 to 2π.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Why does current in a steady state not flow in a capacitor connected across a battery? However momentary current does flow during charging or discharging of the capacitor. Explain.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is – 13∙6 eV. If an electron makes a transition from an energy level – 1∙51 eV to – 3∙4 eV, calculate the wavelength of the spectral line emitted and name the series of hydrogen spectrum to which it belongs.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Find the condition under which the charged particles moving with different speeds in the presence of electric and magnetic field vectors can be used to select charged particles of a particular speed.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Advertisements
Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. If µ for water is 1.33, find the wavelength, frequency and speed of the refracted light.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is 20 cm.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Define mutual inductance.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Write the S.I. unit of mutual inductance.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Derive an expression for the mutual inductance of two long co-axial solenoids of same length wound one over the other,
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Define self-inductance of a coil.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Obtain an expression for the energy stored in a solenoid of self-inductance ‘L’ when the current through it grows from zero to ‘I’.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Write the principle of working of a metre bridge
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
In a metre bridge, the balance point is found at a distance l1 with resistances R and S as shown in the figure.An unknown resistance X is now connected in parallel to the resistance S and the balance point is found at a distance l2. Obtain a formula for X in terms of l1, l2 and S.

Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Draw a circuit diagram of a transistor amplifier in CE configuration.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Derive an expression for voltage gain of the amplifier and hence show that the output voltage is in opposite phase with the input voltage.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
The potential difference applied across a given resistor is altered so that the heat produced per second increases by a factor of 9. By what factor does the applied potential difference change?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
In the figure shown, an ammeter A and a resistor of 4 Ω are connected to the terminals of the source. The emf of the source is 12 V having an internal resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the voltmeter and ammeter readings.
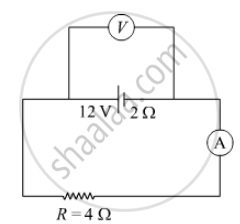
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Draw a block diagram of generalized communication system.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Write the functions of the following in communication systems:
Transmitter
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Write the functions of each of the following in communication system : Channel
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Write the functions of the following in communication systems:
Receiver
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the formation of a final image by a compound microscope at least distance of distinct vision
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
You are given the following three lenses. Which two lenses will you use as an eyepiece and as an objective to construct a compound microscope?
| Lenses | Power (D) | Aperture (cm) |
| L1 | 3 | 8 |
| L2 | 6 | 1 |
| L3 | 10 | 1 |
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Define resolving power of a microscope and write one factor on which it depends
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
The following graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal :
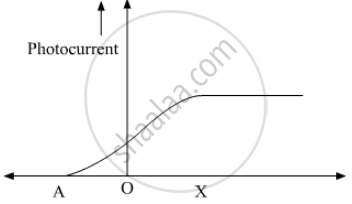
(a) Identify the variable X on the horizontal axis.
(b) What does the point A on the horizontal axis represent?
(c) Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation v1, v2 and v3 (v1 > v2 > v3) for same intensity.
(d) Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I1 > I2 > I3) having same frequency.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Advertisements
Two identical parallel plate capacitors A and B are connected to a battery of V volts with the switch S closed. The switch is now opened and the free space between the plates of the capacitors is filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant K. Find the ratio of the total electrostatic energy stored in both capacitors before and after the introduction of the dielectric.
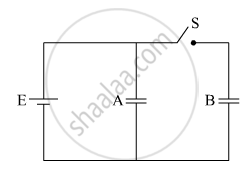
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
How is amplitude modulation achieved?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
The frequencies of two side bands in an AM wave are 640 kHz and 660 kHz respectively. Find the frequencies of carrier and modulating signal. What is the bandwidth required for amplitude modulation?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
In the following diagram 'S' is a semiconductor. Would you increase or decrease the value of R to keep the reading of the ammeter A constant when S is heated? Give reason for your answer.
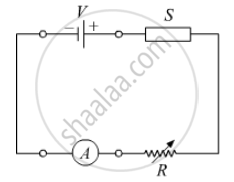
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
With the help of a neat circuit diagram, explain the working of a photodiode.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw its I – V characteristics of photodiode
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
State Biot – Savart law.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Express Biot – Savart law in the vector form.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Two identical circular coils, P and Q each of radius R, carrying currents 1 A and √3A respectively, are placed concentrically and perpendicular to each other lying in the XY and YZ planes. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the centre of the coils.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Asha's mother read an article in the newspaper about a disaster that took place at Chernobyl. She could not understand much from the articles and asked a few questions from Asha regarding the article. Asha tried to answer her mother's questions based on what she learnt in Class XII Physics.
(a) What was the installation at Chernobyl where the disaster took place? What according to you, was the cause of this disaster?
(b) Explain the process of release of energy in the installation at Chernobyl.
(c) What according to you, were the values displayed by Asha and her mother?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
A device 'X' is connected to an ac source V = V0 sin ωt. The variation of voltage, current and power in one cycle is shown in the following graph:

(a) Identify the device 'X'.
(b) Which of the curves A, B and C represent the voltage , current and the power consumed in the circuit? Justify your answer.
(c) How does its impedance vary with frequency of the ac source? Show graphically.
(d) Obtain an expression for the current in the circuit and its phase relation with ac voltage.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Draw a labelled diagram of an ac generator.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Obtain the expression for the emf induced in the rotating coil of N turns each of cross-sectional area A, in the presence of a magnetic field `vecB` .
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Use Huygens' principle to verify the laws of refraction.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
How is linearly polarised light obtained by the process of scattering of light. Find the Brewster angle for air – glass interface, when the refractive index of glass = 1.5.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Two thin convex lenses L1 and L2 of focal lengths f1 and f2, respectively, are placed coaxially in contact. An object is placed at a point beyond the focus of lens L1. Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation by the combination and hence derive the expression for the focal length of the combined system.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A ray of light passing from air through an equilateral glass prism undergoes minimum deviation when the angle of incidence is 3/4 th of the angle of prism. Calculate the speed of light in the prism.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
(a) Derive an expression for the electric field E due to a dipole of length '2a' at a point distant r from the centre of the dipole on the axial line.
(b) Draw a graph of E versus r for r >> a.
(c) If this dipole were kept in a uniform external electric field E0, diagrammatically represent the position of the dipole in stable and unstable equilibrium and write the expressions for the torque acting on the dipole in both the cases.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Use Gauss's law to find the electric field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet. What is the direction of field for positive and negative charge densities?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
An infinitely large thin plane sheet has a uniform surface charge density +σ. Obtain the expression for the amount of work done in bringing a point charge q from infinity to a point, distant r, in front of the charged plane sheet.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2016 - 2017
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2017 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
