Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, if the incident violet light is replaced by red light? Give reason.
उत्तर १
Refractive index of the prism (μ) is inversely proportional to the wavelength of the incident light (λ) i.e.
μ ∝ 1/λ ...(i)
Also, minimum deviation(δm) is related to the refractive index as:
δm ∝ μ
from (i)
δm ∝ 1/λ ...(ii)
As we know wavelength of red light is more than the violet light. Therefore, using (ii), we can conclude that the angle of minimum deviation for red light is less than the violet light.
उत्तर २
The angle of minimum deviation is given by δm = ( n21 - 2 ) A
If voilet light light is replaced by red light its refractive index decreses and angle of minimum deviation decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
At what angle should a ray of light be incident on the face of a prism of refracting angle 60° so that it just suffers total internal reflection at the other face? The refractive index of the material of the prism is 1.524.
A ray of light passing from air through an equilateral glass prism undergoes minimum deviation when the angle of incidence is 3/4 th of the angle of prism. Calculate the speed of light in the prism.
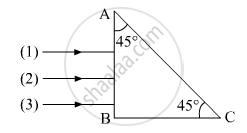
Three rays (1, 2, 3) of different colours fall normally on one of the sides of an isosceles right angled prism as shown. The refractive index of prism for these rays is 1.39, 1.47 and 1.52 respectively. Find which of these rays get internally reflected and which get only refracted from AC. Trace the paths of rays. Justify your answer with the help of necessary calculations.
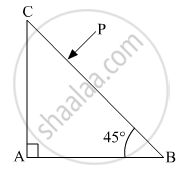
Trace the path of the ray (P) of light passing through the glass prism as shown in the figure. The prism is made of glass with critical angle ic = 41°.
Can you ever have a situation in which a light ray goes undeviated through a prism?
Find the angle of minimum deviation for an equilateral prism made of a material of refractive index 1.732. What is the angle of incidence for this deviation?
A small object is embedded in a glass sphere (μ = 1.5) of radius 5.0 cm at a distance 1.5 cm left to the centre. Locate the image of the object as seen by an observer standing (a) to the left of the sphere and (b) to the right of the sphere.
Answer the following question.
Calculate the angle of emergence (e) of the ray of light incident normally on the face AC of a glass prism ABC of refractive index `sqrt(3)`. How will the angle of emergence change qualitatively, if the ray of light emerges from the prism into a liquid of refractive index 1.3 instead of air?
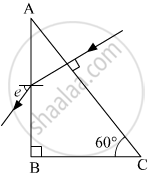
A triangular prism of glass is shown in the figure. A ray incident normally to one face is totally internally reflected. If θ is 45°, then the index of refraction of the glass is ______.
Two concave refracting surfaces of equal radii of curvature face each other in the air as shown in the figure. The point object O is placed midway between the centre and one of the poles. Then the separation between the images of O formed by each refracting surface is ______.