Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Can you ever have a situation in which a light ray goes undeviated through a prism?
उत्तर
There is only one such situation. Light rays go undeviated through a prism only when the prism is kept in a medium that has the same refractive index as that of the prism itself. In all other situations, there will always be some minimum deviation in the path of a light ray passing through the prism.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, if the incident violet light is replaced by red light? Give reason.
Find the angle of incidence at face AB so that the emergent ray grazes along the face AC.
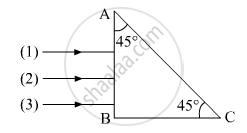
Three rays (1, 2, 3) of different colours fall normally on one of the sides of an isosceles right angled prism as shown. The refractive index of prism for these rays is 1.39, 1.47 and 1.52 respectively. Find which of these rays get internally reflected and which get only refracted from AC. Trace the paths of rays. Justify your answer with the help of necessary calculations.
A ray of light, incident on an equilateral prism `(μ_g = sqrt3)`moves parallel to the base line of the prism inside it. Find the angle of incidence for this ray.
If a piece of paper is placed at the position of a virtual image of a strong light source, will the paper burn after sufficient time? What happens if the image is real? What happens if the image is real but the source is virtual?
Suggest a method to produce a rainbow in your house.
A flint glass prism and a crown glass prism are to be combined in such a way that the deviation of the mean ray is zero. The refractive index of flint and crown glasses for the mean ray are 1.620 and 1.518 respectively. If the refracting angle of the flint prism is 6.0°, what would be the refracting angle of the crown prism?
Find the angle of minimum deviation for an equilateral prism made of a material of refractive index 1.732. What is the angle of incidence for this deviation?
A small object is embedded in a glass sphere (μ = 1.5) of radius 5.0 cm at a distance 1.5 cm left to the centre. Locate the image of the object as seen by an observer standing (a) to the left of the sphere and (b) to the right of the sphere.
Answer the following question.
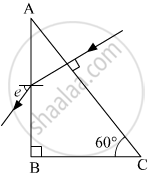
Calculate the angle of emergence (e) of the ray of light incident normally on the face AC of a glass prism ABC of refractive index `sqrt(3)`. How will the angle of emergence change qualitatively, if the ray of light emerges from the prism into a liquid of refractive index 1.3 instead of air?
A prism is made of glass of unknown refractive index. A parallel beam of light is incident on the face of the prism. The angle of minimum deviation is measured to be 40°. What is the refractive index of the material of the prism? The refracting angle of the prism is 60°. If the prism is placed in water (refractive index 1.33), predict the new angle of minimum deviation of a parallel beam of light.
The refractive index of a prism whose angle A = 60° is `sqrt2`. Then the angle of minimum deviation δm will be ______.
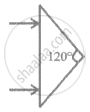
An isosceles prism of angle 120° has a refractive index 1.44. Two parallel monochromatic rays enter the prism parallel to each other in air as shown. The rays emerge from the opposite faces:
The maximum value of the index of refraction of a material of a prism which allows the passage of light through it when the refracting angle of the prism is A is ______.
Two concave refracting surfaces of equal radii of curvature face each other in the air as shown in the figure. The point object O is placed midway between the centre and one of the poles. Then the separation between the images of O formed by each refracting surface is ______.
A ray of light is refracted by a glass prism. Obtain an expression for the refractive index of the glass in terms of the angle of prism A and the angle of minimum deviation δm.
