Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Is the formula "Real depth/Apparent depth = μ" valid if viewed from a position quite away from the normal?
उत्तर
No, because this formula is only valid when the angles of incidence and refraction are small. When the angles of incidence and refraction are large, we cannot use relations sini = tani and sinr = tanr to derive the formula for the apparent depth.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Light of wavelength 5000 Å propagating in air gets partly reflected from the surface of water. How will the wavelengths and frequencies of the reflected and refracted light be affected?
A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm in air. It is made of a material of refractive index 1·6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1·3, find its new focal length.
Why does a diamond shine more than a glass piece cut to the same shape?
A narrow beam of light passes through a slab obliquely and is then received by an eye following figure. The index of refraction of the material in the slab fluctuates slowly with time. How will it appear to the eye? The twinkling of stars has a similar explanation.
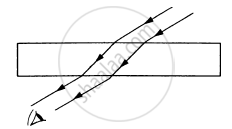
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
A vessel contains water up to a height of 20 cm and above it an oil up to another 20 cm. The refractive indices of the water and the oil are 1.33 and 1.30 respectively. Find the apparent depth of the vessel when viewed from above.
A point ‘O’ marked on the surface of a glass sphere of diameter 20 cm is viewed through glass from the position directly opposite to the point O. If the refractive index of the glass is 1.5, find the position of the image formed. Also, draw the ray diagram for the formation of the image.
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
Why do stars twinkle?
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
What is mirage?
The critical angle for a ray of light from glass to air is 'θ' and refractive index of glass with respect to air is 'n'. If a ray of light is incident from air to glass at an angle 'θ', then corresponding angle of refraction is ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
Light travels in two media A and B with speeds 1.8 × 108 ms−1 and 2.4 × 108 ms−1 respectively. Then the critical angle between them is:
Show that for a material with refractive index `µ ≥ sqrt(2)`, light incident at any angle shall be guided along a length perpendicular to the incident face.
A beam of light travels from air into a medium. Its speed and wavelength in the medium are 1.5 × 108 ms-1 and 230 nm respectively. The wavelength of light in the air will be ______.
