Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Is the formula "Real depth/Apparent depth = μ" valid if viewed from a position quite away from the normal?
Solution
No, because this formula is only valid when the angles of incidence and refraction are small. When the angles of incidence and refraction are large, we cannot use relations sini = tani and sinr = tanr to derive the formula for the apparent depth.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in the glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Figure (c)].
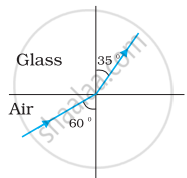 |
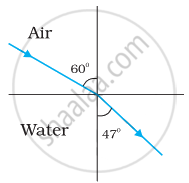 |
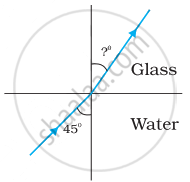 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
Double-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 20 cm?
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
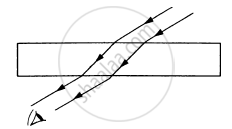
A narrow beam of light passes through a slab obliquely and is then received by an eye following figure. The index of refraction of the material in the slab fluctuates slowly with time. How will it appear to the eye? The twinkling of stars has a similar explanation.
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
If the light moving in a straight line bends by a small but fixed angle, it may be a case of
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) diffraction
(d) dispersion.
Figure shows a transparent hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm made of a material of refractive index 2.0. (a) A narrow beam of parallel rays is incident on the hemisphere as shown in the figure. Are the rays totally reflected at the plane surface? (b) Find the image formed by the refraction at the first surface. (c) Find the image formed by the reflection or by the refraction at the plane surface. (d) Trace qualitatively the final rays as they come out of the hemisphere.

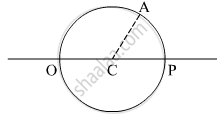
What is relative refractive index?
What is looming?
Obtain the equation for radius of illumination (or) Snell’s window.
Obtain the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab.
When a light ray is incident on a prism at an angle of 45°, the minimum deviation is obtained. If refractive index of material of prism is `sqrt2`, then angle of prism will be ______.
`sin pi/4=1/sqrt2, sin30^circ=cos60^circ=1/2`
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
If `"^imu_j` represents refractive index, when a light ray goes from medium i to medium j, then the product `"^2mu_1 xx ^3mu_2 xx ^4mu_3` is equal to ______.
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
Show that for a material with refractive index `µ ≥ sqrt(2)`, light incident at any angle shall be guided along a length perpendicular to the incident face.
A beam of light travels from air into a medium. Its speed and wavelength in the medium are 1.5 × 108 ms-1 and 230 nm respectively. The wavelength of light in the air will be ______.
