Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
Solution
Actual depth of the pin, d = 15 cm
Apparent depth of the pin = d'
Refractive index of glass, μ = 1.5
Ratio of actual depth to the apparent depth is equal to the refractive index of glass, i.e.
`μ = "d"/"d'"`
∴ d' = `"d"/μ`
= `15/1.5`
= 10 cm
The distance at which the pin appears to be raised = d' − d = 15 − 10 = 5 cm
For a small angle of incidence, this distance does not depend upon the location of the slab.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
- Figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fibre of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for which total reflections inside the pipe take place, as shown in the figure?
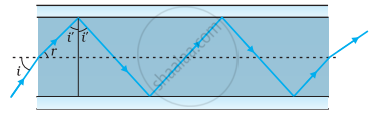
- What is the answer if there is no outer covering of the pipe?
A fish which is at a depth of l2 em .in water `(mu = 4/3)` is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. Its apparent depth as observed: by the observer is:
a) 3 cm
b) 9 cm
c) 12 cm
d) 16 cm
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
A glass lens of refractive index 1.45 disappears when immersed in a liquid. What is the value of refractive index of the liquid?
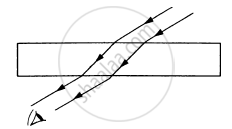
A narrow beam of light passes through a slab obliquely and is then received by an eye following figure. The index of refraction of the material in the slab fluctuates slowly with time. How will it appear to the eye? The twinkling of stars has a similar explanation.
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
The refractive index of a material changes by 0.014 as the colour of the light changes from red to violet. A rectangular slab of height 2.00 cm made of this material is placed on a newspaper. When viewed normally in yellow light, the letters appear 1.32 cm below the top surface of the slab. Calculate the dispersive power of the material.
If the light moving in a straight line bends by a small but fixed angle, it may be a case of
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) diffraction
(d) dispersion.
Consider the situation in figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is μ. (a) At what distance(s) from itself will the fish see the image(s) of the eye? (b) At what distance(s) from itself will the eye see the image(s) of the fish.

Stars twinkle due to ______.
What is optical path? Obtain the equation for optical path of a medium of thickness d and refractive index n.
What is angle of deviation due to refraction?
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
What is mirage?
When a light ray is incident on a prism at an angle of 45°, the minimum deviation is obtained. If refractive index of material of prism is `sqrt2`, then angle of prism will be ______.
`sin pi/4=1/sqrt2, sin30^circ=cos60^circ=1/2`
If `"^imu_j` represents refractive index, when a light ray goes from medium i to medium j, then the product `"^2mu_1 xx ^3mu_2 xx ^4mu_3` is equal to ______.
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because ______.
- the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
- the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
- some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
- water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
