Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
Solution
Let SS' represent the surface separating media 1 and 2 of refractive indices n1 and n2, respectively. Let c1 and c2 be the velocities of light in the two media. The second medium is optically denser than the first, hence c1 > c2.
APB is the incident wavefront. By the time the disturbance at B reaches C, the secondary wavelet from A has travelled a distance of AD = c2t, where t is the time it took the waves to travel the distance of BC. Therefore, BC= c1 t and AD= c2t.· With A as the centre and radius AD(= c2t), we draw a sphere and a tangent CD to the sphere is also drawn from the point C. Thus, CD represents the refracted plane wavefront. To prove that CD is the common wavefront, it is enough to show that in the time the disturbance travels from B to C or A to D, the disturbance at P reaches L. With M as the centre, we draw a sphere such that CD happens to be the tangent of the sphere.
From the similar triangles ACD and MCL,
`("AD")/("ML") = ("AC")/("MC")` ...(i)
Similarly, from similar triangles (ACE and MCN),
`("AE")/("MN") = ("AC")/("MC")` ...(ii)
From (i) and (ii),
`("AD")/("ML") = ("AE")/("MN")`
or `("AE")/("AD") = ("MN")/("ML")`
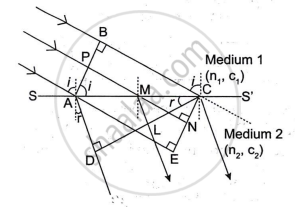
∵ AE = BC = c1t and AD = c2t, we can write,
`("AE")/("AD") = (c_1t)/(c_2t) = ("MN")/("ML")`
or `("BC")/("AD") = ("MN")/("ML") = (c_1)/(c_2)` ...(iii)
The radius of the secondary wavefront for point A is therefore AD, while the radius of the secondary wavefront for point M is ML.
Let r and i represent the angles of refraction and incidence, respectively.
From triangle ABC and ACD,
`sini/sinr = ("BC"/"AC")/("AD"/"AC") = ("BC")/("AD") = (c_1t)/(c_2t) = c_1/c_2 = ""_1n_2`
1n2 is constant and is called the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium. So, `sini/sinr` = constant
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Light of wavelength 5000 Å propagating in air gets partly reflected from the surface of water. How will the wavelengths and frequencies of the reflected and refracted light be affected?
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
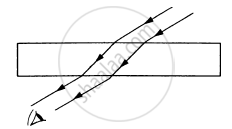
A narrow beam of light passes through a slab obliquely and is then received by an eye following figure. The index of refraction of the material in the slab fluctuates slowly with time. How will it appear to the eye? The twinkling of stars has a similar explanation.
The refractive index of a material changes by 0.014 as the colour of the light changes from red to violet. A rectangular slab of height 2.00 cm made of this material is placed on a newspaper. When viewed normally in yellow light, the letters appear 1.32 cm below the top surface of the slab. Calculate the dispersive power of the material.
Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.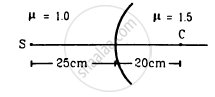
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium of refractive index n falls, on a surface separating the medium from air at an angle of incidents of 45°. The ray can undergo total internal reflection for the following n.
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
What is critical angle and total internal reflection?
What is mirage?
