Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.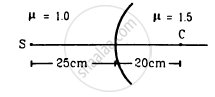
Solution
Given,
Let the refractive indices of two mediums be μ1=1.0 and μ2 =1.5
Point C is the centre of curvature, the distance between C and the pole is 20 cm.
Therefore, radius of curvature (R) = 20 cm
Distance between source S and pole is 25 cm.
Therefore, object distance (u) = −25
\[\frac{\mu_2}{v} - \frac{\mu_1}{u} = \frac{\mu_2 - \mu_1}{R}\] 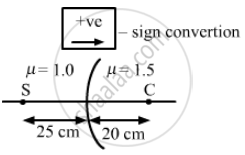
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1 . 5}{v} - \frac{1}{( - 25)} = \frac{0 . 5}{20}\]
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1 . 5}{v} = \frac{- 3}{200}\]
\[\therefore v = - \frac{200 \times 1 . 5}{0 . 3 \times 10} = - 100\]
Hence, the required location of the image is 100 cm from the pole and on the side of S.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Light of wavelength 5000 Å propagating in air gets partly reflected from the surface of water. How will the wavelengths and frequencies of the reflected and refracted light be affected?
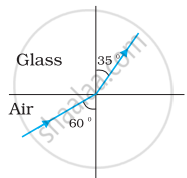
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in the glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Figure (c)].
 |
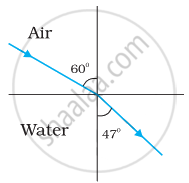 |
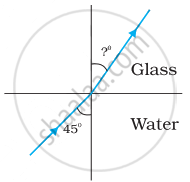 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
A diver under water, looks obliquely at a fisherman standing on the bank of a lake. Would the fisherman look taller or shorter to the diver than what he actually is?
Why does a diamond shine more than a glass piece cut to the same shape?
A laser light is focussed by a converging lens. Will there be a significant chromatic aberration?
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
A vessel contains water up to a height of 20 cm and above it an oil up to another 20 cm. The refractive indices of the water and the oil are 1.33 and 1.30 respectively. Find the apparent depth of the vessel when viewed from above.
A converging beam of light travelling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1 . 5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of the image. Also draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
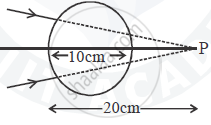
Choose the correct option.
There are different fish, monkeys, and water of the habitable planet of the star Proxima b. A fish swimming underwater feels that there is a monkey at 2.5 m on the top of a tree. The same monkey feels that the fish is 1.6 m below the water surface. Interestingly, height of the tree and the depth at which the fish is swimming are exactly same. Refractive index of that water must be
Stars twinkle due to ______.
What is angle of deviation due to refraction?
Why do stars twinkle?
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
What is looming?
Obtain the equation for radius of illumination (or) Snell’s window.
Derive the equation for acceptance angle and numerical aperture, of optical fiber.
Obtain the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab.
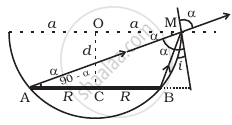
A circular disc of radius ‘R’ is placed co-axially and horizontally inside an opaque hemispherical bowl of radius ‘a’ (Figure). The far edge of the disc is just visible when viewed from the edge of the bowl. The bowl is filled with transparent liquid of refractive index µ and the near edge of the disc becomes just visible. How far below the top of the bowl is the disc placed?