Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.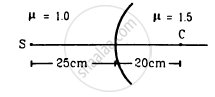
उत्तर
Given,
Let the refractive indices of two mediums be μ1=1.0 and μ2 =1.5
Point C is the centre of curvature, the distance between C and the pole is 20 cm.
Therefore, radius of curvature (R) = 20 cm
Distance between source S and pole is 25 cm.
Therefore, object distance (u) = −25
\[\frac{\mu_2}{v} - \frac{\mu_1}{u} = \frac{\mu_2 - \mu_1}{R}\] 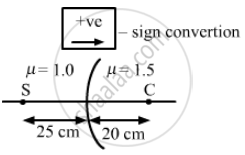
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1 . 5}{v} - \frac{1}{( - 25)} = \frac{0 . 5}{20}\]
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1 . 5}{v} = \frac{- 3}{200}\]
\[\therefore v = - \frac{200 \times 1 . 5}{0 . 3 \times 10} = - 100\]
Hence, the required location of the image is 100 cm from the pole and on the side of S.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
Determine the value of the angle of incidence for a ray of light travelling from a medium of refractive index \[\mu_1 = \sqrt{2}\] into the medium of refractive index \[\mu_2 = 1\] so that it just grazes along the surface of separation.
Is the formula "Real depth/Apparent depth = μ" valid if viewed from a position quite away from the normal?
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
The refractive index of a material changes by 0.014 as the colour of the light changes from red to violet. A rectangular slab of height 2.00 cm made of this material is placed on a newspaper. When viewed normally in yellow light, the letters appear 1.32 cm below the top surface of the slab. Calculate the dispersive power of the material.
A pole of length 1.00 m stands half dipped in a swimming pool with water level 50.0 cm higher than the bed. The refractive index of water is 1.33 and sunlight is coming at an angle of 45° with the vertical. Find the length of the shadow of the pole on the bed.
An object P is focussed by a microscope M. A glass slab of thickness 2.1 cm is introduced between P and M. If the refractive index of the slab is 1.5, by what distance should the microscope be shifted to focus the object again?
Figure shows a transparent hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm made of a material of refractive index 2.0. (a) A narrow beam of parallel rays is incident on the hemisphere as shown in the figure. Are the rays totally reflected at the plane surface? (b) Find the image formed by the refraction at the first surface. (c) Find the image formed by the reflection or by the refraction at the plane surface. (d) Trace qualitatively the final rays as they come out of the hemisphere.

A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
Choose the correct option.
There are different fish, monkeys, and water of the habitable planet of the star Proxima b. A fish swimming underwater feels that there is a monkey at 2.5 m on the top of a tree. The same monkey feels that the fish is 1.6 m below the water surface. Interestingly, height of the tree and the depth at which the fish is swimming are exactly same. Refractive index of that water must be
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
Stars twinkle due to ______.
What is critical angle and total internal reflection?
How does an endoscope work?
For a rectangular slab, refraction takes place at ______.
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Figure). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by.
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
