Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
उत्तर
Given,
Focal length of the convex lens, fd = 20 cm
Focal length of the concave lens, fc = 10 cm
Beam diameter of the incident light, d = 5.0 mm
Distance between both the lenses is 10 cm.
As per the question, the incident beam of light is parallel to the principal axis.
Let it be incident on the convex lens.
Now, let B be the focus of the convex lens where the image by the convex lens should be formed.
For the concave lens,
Object distance (u) = + 10 cm (Virtual object is on the right of concave lens.)
Focal length, fc = − 10 cm
Using the lens formula,
\[\frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[\Rightarrow\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{- 10}+\frac{1}{+ 10}=\infty\]
\[\Rightarrow v=\infty\]
Thus, after refraction in the concave lens, the emergent beam becomes parallel.
As shown, in triangles XYB and PQB,
\[\frac{PQ}{XY} = \frac{RB}{ZB} = \frac{10}{20} = \frac{1}{2}\]
\[PQ = \frac{1}{2} \times 5 = 2 . 5 \text{ mm }\]
Thus, the beam diameter of the emergent light is 2.5 mm.
Similarly, we can prove that if the beam of light is incident on the side of the concave lens, the beam diameter (d) of the emergent light will be 1 cm.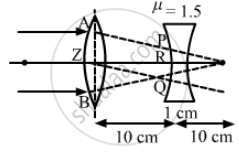
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Light of wavelength 5000 Å propagating in air gets partly reflected from the surface of water. How will the wavelengths and frequencies of the reflected and refracted light be affected?
- Figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fibre of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for which total reflections inside the pipe take place, as shown in the figure?
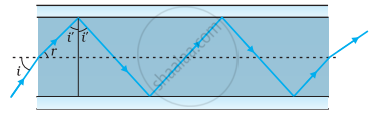
- What is the answer if there is no outer covering of the pipe?
Light incident normally on a plane mirror attached to a galvanometer coil retraces backward as shown in Figure. A current in the coil produces a deflection of 3.5° of the mirror. What is the displacement of the reflected spot of light on a screen placed 1.5 m away?

A pole of length 1.00 m stands half dipped in a swimming pool with water level 50.0 cm higher than the bed. The refractive index of water is 1.33 and sunlight is coming at an angle of 45° with the vertical. Find the length of the shadow of the pole on the bed.
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
Stars twinkle due to ______.
Why do stars twinkle?
What is critical angle and total internal reflection?
How does an endoscope work?
Obtain the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab.
A ray of light travels from air to water to glass and aga in from glass to air. Refractive index of water with respect to air is 'x' glass with respect to water is 'y' and air with respect to glass is 'z'. which one of the following is correct?
A light travels through water in the beaker. The height of water column is 'h'. Refractive index of water is 'μw'. If c is velocity of light in air, the time taken by light to travel through water will ______.
A ray of light passes through equilateral prism such that the angle of incidence is equal to angle of emergence and each of these angles is equal to `(3/4)^"th"` the angle of prism. The angle of deviation is ______.
The critical angle is maximum when light travels from ______.
`(a^mu"w"=4/3,a^mug=3/2)`
Light travels from an optically denser medium 'A' into the optically rarer medium 'B' with speeds 1.8 × 108 m/s and 2.7 × 108 m/s respectively. Then critical angle between them is ______.
(µ1 and µ2 are the refractive indices of media A and B respectively.)
For a rectangular slab, refraction takes place at ______.
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because ______.
- the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
- the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
- some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
- water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
Three immiscible liquids of densities d1 > d2 > d3 and refractive indices µ1 > µ2 > µ3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is `h/3`. A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
